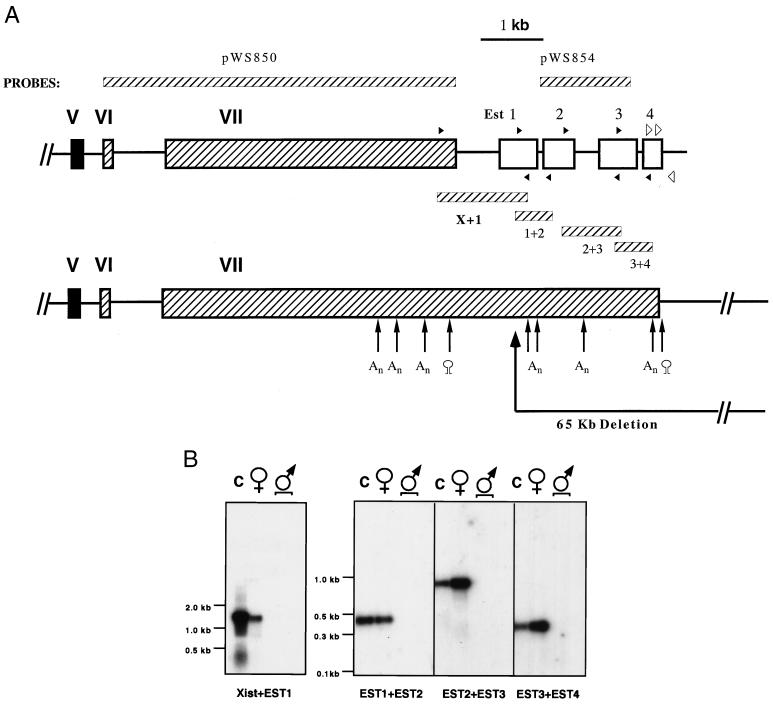
Figure 2.
New structure of the 3′end Xist. (A) The four ESTs (EST1≈4) are mapped relative to exon VII of Xist (GenBank accession nos. of EST1 ≈ 4: AA543875, AA221611, AA690387§, and R74734, respectively). PCR fragments synthesized by using primers whose locations are marked by closed arrowheads are shown to demonstrate the colinearity of all the ESTs. Locations of primers used to determine the end of the Xist transcript are marked by open arrowheads. Probes used for Northern blots and RNA–FISH (pWS854, pWS850) are also indicated. Consensus sequences for polyadenylation (An) and sequences of putative stem and loop structures are also localized. The 65-kb deletion created by Clerc and Avner (12) begins from the ScaI site (marked with heavy arrow) in the EST1. EST fragments were recovered as described in Experimental Procedures. (B) All the ESTs are colinear with Xist. All PCR products were sequenced. For the purpose of this figure, the PCR fragments for Xist + EST1 and for EST1 + EST2, EST2 + EST3, and EST3 + EST4 were electrophoresed in 0.8% and 2% agarose gels, respectively, transferred to nylon membranes, and hybridized with individual fragments (probes for this figure, Xist, EST1, EST2, and EST3, respectively). (C) YAC116 (genomic DNA); ♀, female mouse lung cDNA library; ♂, male mouse brain and male heart cDNA libraries. Approximate DNA sizes are marked by using either 1-kb marker (GIBCO/BRL) for 0.8% gel or 100-bp marker (NEB, Beverly, MA) for 2% gel. The top of each lane is the origin of migration.
§ Note: Accession no. AA690387 is incorrectly identified as derived from a male mouse cDNA library in GenBank. It is correctly attributed to a female library on the I.M.A.G.E. home page (http://www-bio.llnl.gov/bbrp/image/image.html).