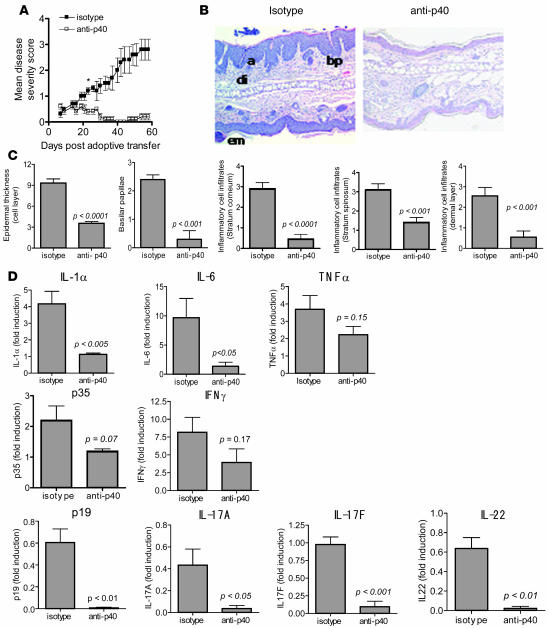
Figure 3. IL-12/IL-23p40 neutralization prevents the development of skin lesions.
(A) Disease severity in CB17 scid/scid mice receiving first CD4+CD45RBhiCD25– cells and subsequently treated with either 0.5 mg of IL-12/23p40 antibody or isotype control antibody (rat IgG2a) i.p. on days 7 and 35 after the adoptive transfer. The mean disease severity scores are reported for 10 mice from each group ± SEM *P < 0.05 starting on day 24, comparing the 2 groups. Data are representative of at least 2 independent experiments. (B) Representative images of H&E-stained sections of ear from recipient CB17 scid/scid mice given an isotype control antibody (left) or IL-12/23p40 antibody (right). Examination of the sections indicates the presence of acanthosis (a), dermal inflammatory infiltrates (di), prominent basilar papilla (bp), and epidermal microabscesses (em) in isotype control antibody–treated mouse skin. Original magnification, ×200. (C) Epidermal thickness and semiquantitative scoring of basilar papillae and inflammatory infiltrates in the stratum corneum, stratum spinosum, and dermal layer of the skin. A section from each mouse ear was scored as follows: 0, within normal limits; 1, minimal; 2, mild; 3, moderate; 4, marked; and 5, severe. The means ± SEM are shown, with n = 10 for each group. (D) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis for each indicated cytokine in RNA isolated from mouse ear at the end of the study. Results reported as mean ± SEM. Data are representative of at least 2 independent experiments, with n = 10 for each group.