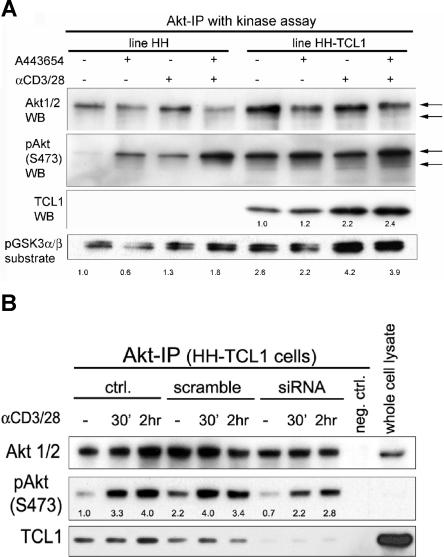
Figure 5.
TCL1 introduction into leukemic T cells influences AKT phosphorylation and kinase activity. (A) Transfection of TCL1 into the sTCR+ mature T-cell leukemia line HH augmented baseline and TCR-induced AKT phosphoactivation, and increased phosphorylation of the AKT target GSK3α/β (2.6-fold at baseline and 1.3- to 4.2-fold TCR induced). Similar to primary T-PLL tumor cells, TCR cross-linking also increased the amount of TCL1 complexed with AKT by 2.2-fold. Preincubation of tumor cells with the AKT inhibitor A443654 at 0.5 μM leads to slightly decreased GSK3α/β phosphorylation, and a compensatory pAKT increase (kinase assay and Western blot following AKT immunoprecipitation). Indicated are fold changes over the unstimulated DMSO vehicle control. (B) Transient knockdown of TCL1 in the HH-TCL1 cell line reduced baseline levels of activated pAKT in immunoprecipitated complexes compared with control HH-TCL1 (down to 0.7-fold) or cells transfected with scrambled siRNA (assayed at 72 hours). TCL1 knockdown also reduced levels of activated pAKT following TCR engagement for 30 minutes and 2 hours at these time points (ie, 3.3- to 2.2-fold after 30 minutes of simulation).