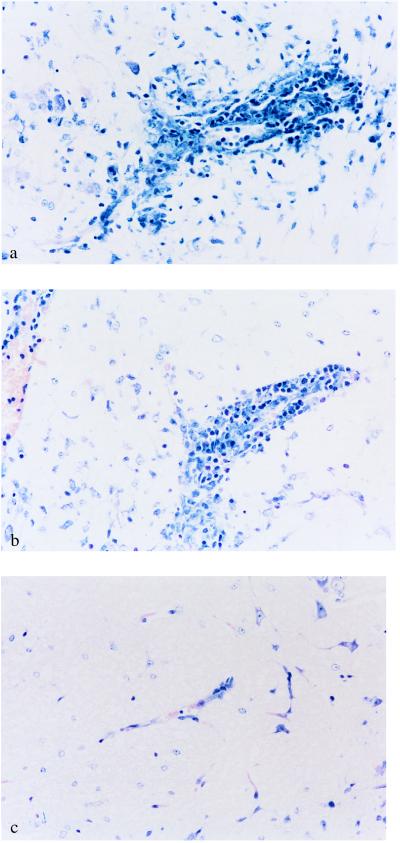
Figure 1.
Prevention of T cell-induced inflammation in the white matter of the CNS by antibodies directed against CD44 and integrin α4 but not L-selectin. Mice were treated continuously with different antibodies for 8 days after adoptive transfer of 5 × 106 MBP peptide Ac1-11-specific T cells. Thereafter, brains of mice treated i.p. with the indicated antibodies or PBS were removed, fixed, sectioned, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Typical regions were photographed. The original magnification was 200×. (a) Histopathology of mice treated with PBS. Shown is perivascular inflammatory infiltrate in the brainstem of a mouse with adoptive EAE. Clinical disease score at the time of death was grade 3. (b) Histopathology of mice treated with mAb MEL-14 (anti-L-selectin). Shown is perivascular inflammatory infiltrate in the brainstem of a mouse with adoptive EAE. Clinical disease score at the time of death was grade 2. (c) Histopathology of mice treated with mAb IM7.8.1 (anti-CD44). Shown is the absence of perivascular infiltrates in the brainstem of a mouse after adoptive transfer of encephalitogenic T cells. Clinical disease score was grade 0.