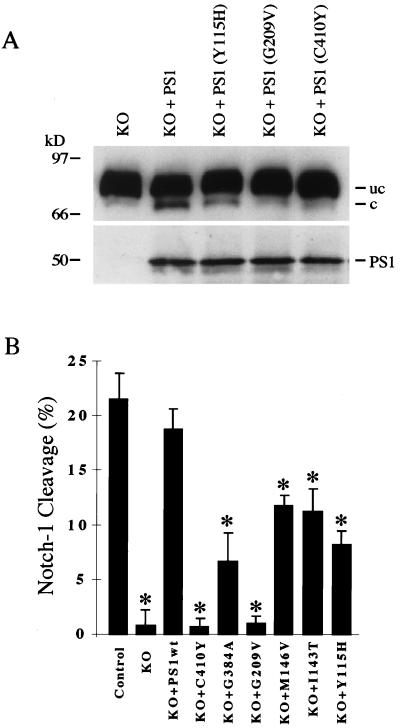
Figure 3.
PS1 mutations associated with familial Alzheimer’s disease impair proteolytic release of the NICD. (A) PS1 mutations associated with familial Alzheimer’s disease impair PS1-induced cleavage. PS1-KO cells transfected with the indicated PS1 mutants exhibit reduced Notch-1 cleavage relative to PS1-KO cells transfected with wild-type PS1. (Upper) NδE immunoblot. (Lower) PS1 immunoblot showing transfected holo-PS1. (B) Quantitative analysis of the effects of six PS1 mutants on Notch-1 cleavage. The ratio of cleaved to uncleaved forms of NδE was quantitated after transfection of NδE in PS1-wt (Control) and PS1-KO (KO) cells and in PS1-KO cells cotransfected with wild-type PS1 (PS1wt) or the indicated PS1 mutants. Note that inhibition of Notch-1 cleavage ranges from 40–60% for PS1 N-terminal mutations to 70–100% for PS1 C-terminal mutations. Notch-1 cleavage was not significantly different between PS1-wt cells and PS1-KO cells transfected with wild-type PS1. Shown is the mean ± SEM, n = 4. ∗, P < 0.05 relative to KO+PS1wt by ANOVA with post-hoc Student–Newman–Keuls test.