Figure 8.
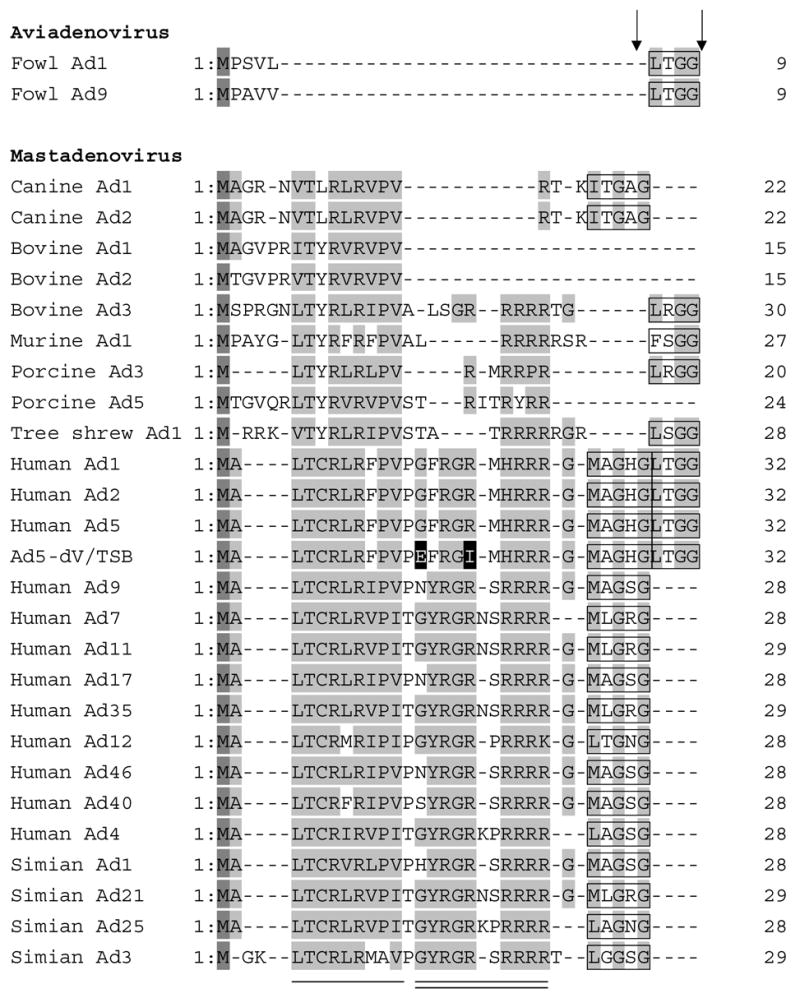
Alignment of the N-terminal domains of Mu protein in selected members of the Adenoviridae family. The amino acid sequences of the N-terminal domains of Mu protein of Adenoviridae were aligned using CLUSTALW software. The two mutated amino acid residues in Ad5-dV/TSB are shown with black background. Methionine residues are shown in a dark gray background and highly conserved residues are indicated by a gray background. The adenoviral protease recognition motif residues for cleavage are indicated by a black box and Ad protease cleavage sites are indicated by arrows. The amino acid sequences of the N-terminal domain of pre-Mu of Adenoviridae were retrieved from the sequence database accession numbers as shown below. fowl Ad1 (AP_000416), fowl Ad9 (AP_000382), canine Ad1 (AP_000057), bovine Ad1 (YP_094038), bovine Ad2 (AP_000012), bovine Ad3 (AAD09726), human Ad1 (AP_000510), human Ad2 (AP_000173), human Ad4 (YP_068030), human Ad5 (AP_000209), human Ad7 (AP_000546), human Ad9 (CAI05967), human Ad11 (AP_000450), human Ad12 (AP_000119), human Ad17 (AP_000148), human Ad35 (AP_000583), human Ad40 (NP_040860), humanAd46 (AAX70957), murine Ad1 (AP_000349), porcine Ad3 (YP_009208), porcine Ad5 (AP_000243), simian Ad1 (YP_213973), simian Ad3 (AAT84625), simian Ad21 (AP_000273), simian Ad25 (AP_000311). The conserved residues in Mastadenoviruses are shown by a single solid line and the conserved residues in human and simian Ads are indicated by a solid double line.
