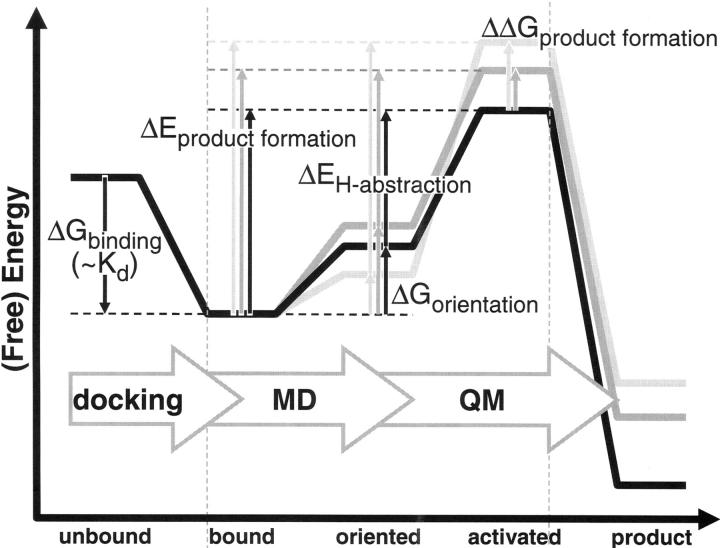
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of different states and corresponding (free) energy differences considered in this study. Docking was used to go from unbound to bound state, but since the free energy of binding (ΔG binding) would be identical for all products formed from a substrate, no free energy barriers (ΔG binding) were calculated for this step. MD was used to calculate the free energy associated with substrate orientation (ΔG orientation). QM was used to calculated the activation barrier for H-abstraction (ΔE H-abstraction). Experimental product formation corresponds to the (free) energy barrier of product formation (ΔE product formation), and can be calculated as the sum of the orientation free energy barrier and the energy barrier of H-abstraction (ΔG orientation + ΔE H-abstraction). Finally, product ratios correspond to the relative free energy of product formation (ΔΔG product formation).