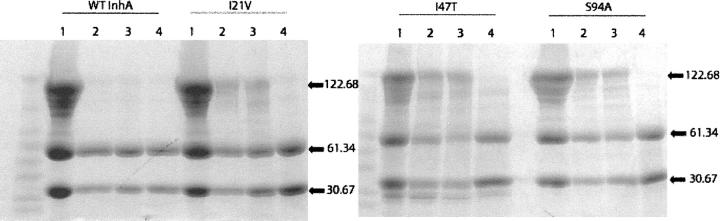
Figure 1.
Cross-linking of wild-type and mutant InhA proteins. Each type of InhA is represented in four lanes, all in the presence of the BS3 cross-linker. (Lane 1) Purified recombinant proteins, all displaying the characteristic monomer, dimer, and tetramer bands. (Lane 2) Proteins in the presence of excess NADH. Wild-type InhA, which has a high affinity for NADH, shows a disappearance of the tetramer band in the presence of cofactor. In contrast all three mutants have a decreased affinity for NADH and retain the tetrameric form. (Lane 3) Proteins in the presence of excess NADH and MnCl2. The presence of MnCl2 does not alter the results found in lane 2. (Lane 4) Proteins under inhibiting conditions, containing NADH, MnCl2, and INH. MnCl2 is used in place of KatG to activate INH. All four proteins have similar affinity for the inhibitory adduct and upon binding, the tetrameric form of the protein can no longer be observed.