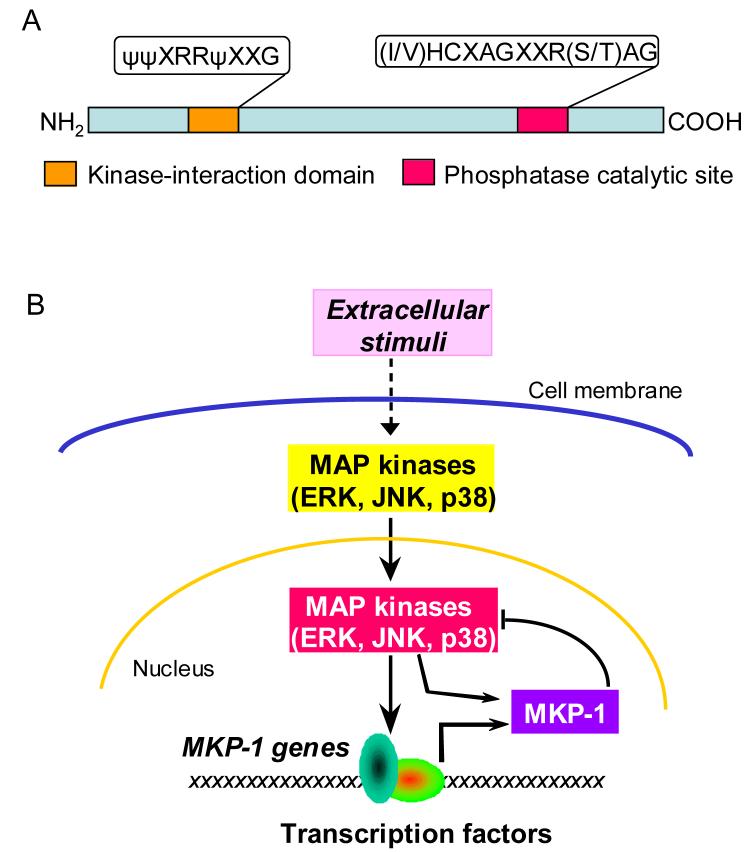
Figure 2. Diagram of the structure and function of MKP-1.
(A) Primary structure of MKP-1. MKP-1 has an amino terminal domain responsible for interaction with MAP kinases. The catalytic domain is located at the carboxyl terminus. (B) Feedback control of MAP kinases by MKP-1. Extracellular stimulation triggers the activation of MAP kinases. Upon activation, MAP kinases translocate to nucleus where they phosphorylate and activate transcription factors, leading to altered gene transcription. Among the genes activated by MAP kinases is MKP-1. MKP-1 protein can dephosphorylate MAP kinases, thus terminating MAP kinase-regulated gene transcription. By phosphorylating MKP-1 protein, MAP kinases can regulate the stability of MKP-1 protein.