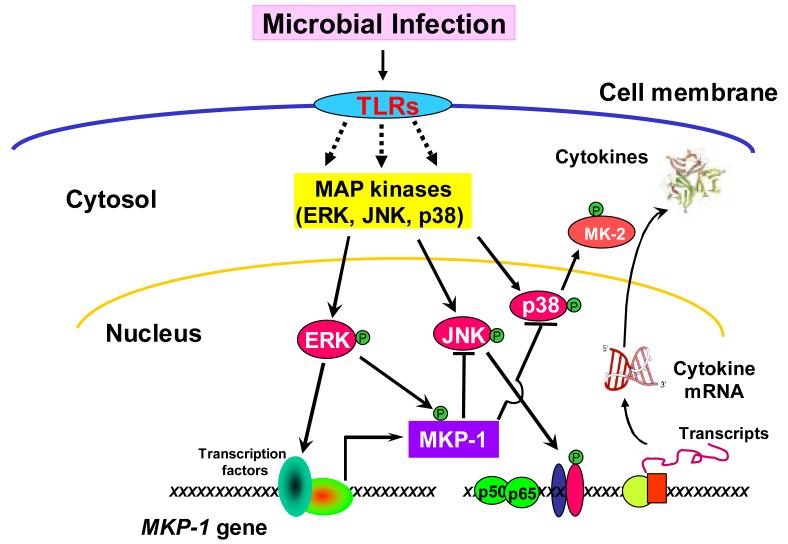
Figure 3. Restraint of pro-inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis by MKP-1.
In response to microbial infection, TLRs initiate a series of signal transduction pathways, including NF-κB and MAP kinase cascades, leading to production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Simultaneously, the signals initiated at the TLRs also induce MKP-1 gene transcription. ERK regulates MKP-1 expression by two mechanisms: by enhanceing MKP-1 gene transcription and by phosphorylating MKP-1 and thereby increasing its half-life. The MKP-1 protein in turn dephosphorylates JNK and p38, thus stopping the perpetuation of the inflammatory cascades and terminating cytokine production.