Figure 8.
miR-200 Target Validation
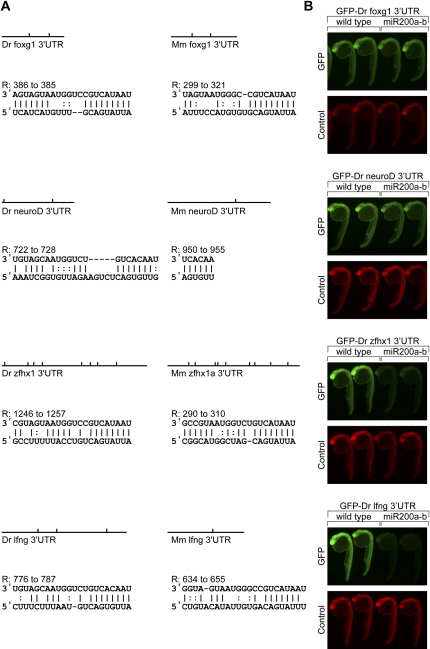
(A) Comparison of conserved miR-200 sites in the 3′UTRs of select miR-200 predicted targets in mouse and zebrafish suggest that miR-200 family members may be sufficient to negatively regulate zfhx1, foxg1, and lfng and may help to downregulate neuroD. Vertical ticks on schematic drawings indicate a predicted miR-200 site, and the alignments correspond to the strongest miR-200 site produced by the miRanda algorithm (Enright et al., 2003).
(B) GFP reporters fused upstream of full-length zebrafish 3′UTRs corresponding to putative targets containing predicted miR-200 binding sites were coinjected with control DsRed mRNA into wild-type zebrafish embryos at the one-cell stage either in the absence or presence of synthetic miR-200a/miR-200b RNA duplex. Fluorescent microscopy shows GFP reporter expression (green) and control DsRed expression (red) at 25–30 hpf, indicating that miR-200 family members are sufficient to downregulate zebrafish zfhx1 and lfng.