Figure 4.
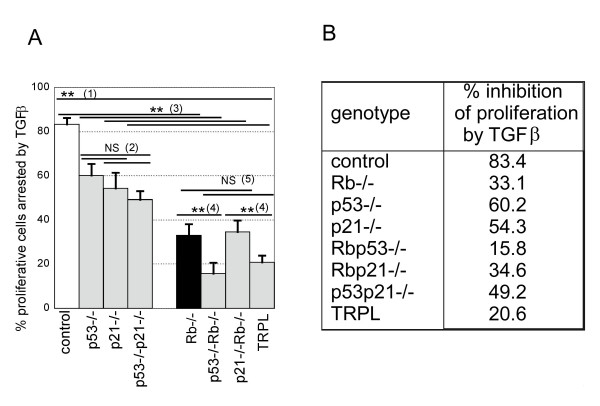
Rb is central to TGFβ inhibition of proliferation via multiple pathways. A. The figure shows the effect of p53, p21Cip1 or Rb deficiency on TGFβ induced cell cycle arrest +/- SDV. The percentage inhibition of proliferation by TGFβ was calculated for 2 (for p53p21-/- and TRPL) to 6 independent experiments and differences analysed by ANOVA (** p < 0.0001; NS non significant). As for all experiments the Rb-null hepatocytes were obtained by infection at the time of plating of the Rb-floxed hepatocytes of corresponding genotypes with adenovirus expressing Cre recombinase. (1) all deficient hepatocytes respond less well to inhibition of proliferation by TGFβ than control cells and Rb deficient has the strongest effect. (2) p53 and p21Cip1deficiency, singly or together have a similar effect on inhibition of proliferation by TGFβ. (3) Rb deletion significantly reduces TGFβ-induced cell cycle arrest regardless of p53 and p21Cip1status (compare control with Rb-/-; p53-/- with p53-/-Rb-/-; p21-/- with p21-/-Rb-/- and p53-/-p21-/- with TRPL). (4) double deficiency in Rb and p53 further decreases hepatocytes responses to TGFβ in term of regulation of proliferation, independently of p21Cip1status. (5) by contrast the effect of TGFβ on hepatocytes deficient in both p21Cip1 and Rb is not significantly different to that of Rb null cells, and this is independent of p53 status. B. corresponding percentages of inhibition of proliferation for each genotype. TRPL: triple null hepatocytes.