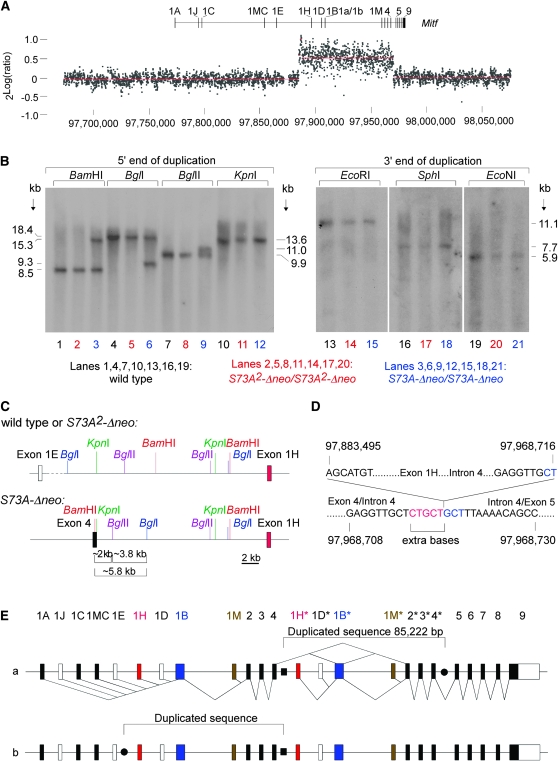
Figure 6.—
Molecular analysis of the duplication. (A) A fine-tiling custom CGH array spanning the indicated region of chromosome 6 (based on sequence release NCBIM:36) was cohybridized with Cy3-labeled DNA from homozygous S73A2-Δneo mice and with Cy5-labeled DNA from S73A-Δneo mice. A copy number difference is seen for a sequence approximately covering positions 97,883,500–97,968,700, extending from upstream of exon 1H to a position between exon 4 and 5. (B) Southern analysis using probes corresponding to the 5′- and 3′-end of the duplication (left and right, respectively). Probing with the 5′ probe reveals RFLPs in DNA from S73A-Δneo for BamHI, BglI, and BglII, but not for KpnI. Probing with the 3′ probe shows no RFLPs between the different DNAs. (C) Restriction map for wild type or S73A2-Δneo (top) or for S73A-Δneo (bottom) on the basis of the above Southern analyses. The novel restriction fragments indicate the presence of a BamHI–KpnI–BglII–BglI constellation that happens to be present in intron 4 of Mitf. (D) Junction sequences of the inserted partial gene duplication in S73A-Δneo. Five extra bases (red) are found between the intron 4/upstream exon 1H junction. The downstream junction in intron 4 reads exactly like the wild-type sequence. Interestingly, the sequence marked in blue is a direct repeat of the extra sequence marked in red. (E) Two possible arrangements of the insertions of the duplicate. The novel intron 4/upstream exon 1H junction is marked by a solid square, and the potential other junctions by solid circles. In a, the duplicate spanning exons 1H–4 (marked with asterisks) is inserted into intron 4. In b, the duplicate is inserted between exons 1E and 1H. The two possible arrangements, however, are sequence identical. Splice patterns (known and predicted following the insertion of the duplicate) are indicated only for version a.