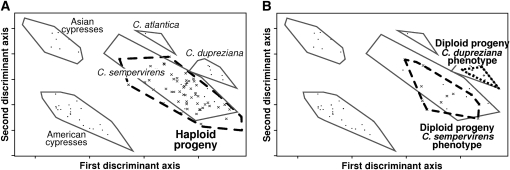
Figure 2.—
Investigation of the genetic origin of progeny using AFLP markers. Only progeny produced by C. dupreziana seed trees planted in ex situ collections were studied. The individual genetic profiles were plotted as supplemental points on the plane defined by the first two axes of a discriminant analysis of cypress species used as a control (the three Mediterranean species C. sempervirens, C. atlantica, and C. dupreziana; one American cypress group; and one Asian cypress group). All haploid progeny (A) were assigned to C. sempervirens. For diploid progeny (B), the genetic assignment either to C. dupreziana or to C. sempervirens was fully consistent with the classification based on the morphological type (Table 1, Figure 1).