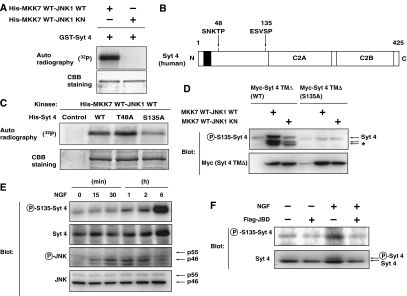
Figure 3.
JNK phosphorylates Syt 4 at Ser135 in vitro and in vivo. (A) Bacterially expressed GST-fused recombinant Syt 4 proteins were incubated with bacterially expressed His-tagged recombinant MKK7-JNK1 fusion proteins (fusion of wild-type MKK7 and wild-type or kinase-negative JNK) in a kinase reaction buffer in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP for 30 min. Phosphorylation of proteins was detected by autoradiography. (B) Potential JNK phosphorylation sites in Syt 4. (C) Bacterially expressed His-tagged Syt 4 proteins (wild-type (WT), T48A or S135A mutants) were incubated with bacterially expressed His-tagged MKK7-JNK1 fusion proteins in a kinase reaction buffer in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. (D) COS1 cells were transfected with an expression vector for either wild-type or S135A Myc-tagged Syt 4 TMΔ (lacking the transmembrane domain), together with an expression vector for MKK7-JNK1. After 24 h, transfected cells were lysed and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies specific for Syt 4 phosphorylated on S135 (P-S135-Syt 4) or antibodies to Myc epitope. The asterisk indicates the position of degradation products of Myc-tagged Syt 4. Note that the amount of Myc-tagged Syt 4 protein was increased in MKK7-JNK1-expressing cells. (E) PC12 cells were cultured for periods as indicated in the presence of 100 ng/ml NGF. The cells were lysed and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies specific for Syt 4 phosphorylated on S135, antibodies to Syt 4, phosphorylated JNK or JNK. (F) PC12 cells were infected with retrovirus encoding JBD or with corresponding control retrovirus (−). Infected cells were incubated for 2 h in the presence or absence of 100 ng/ml NGF. The cells were lysed and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies specific for Syt 4 phosphorylated on S135, or for Syt 4.