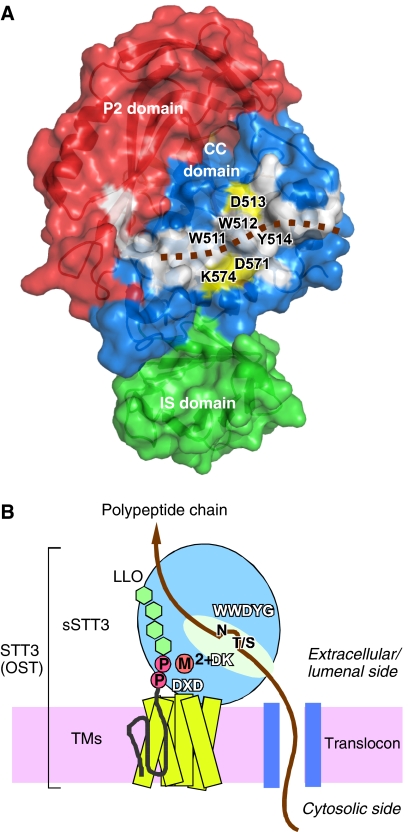
Figure 6.
Large hydrophobic surface and schematic of the overall structure of STT3. (A) Surface representation of the C-terminal soluble domain of P. furiosus STT3, colored according to the domain structure in Figure 3. The P1 domain is behind the molecule, and is not visible. A continuous, hydrophobic surface (white) consists of residues W491, W511, W512, Y514, G515, Y516, W517, I518, L522, L523, Y568, A577, I578, Y580, L581, and Y590 in the CC domain, and L872, F887, and I939 in the P2 domain. The brown dotted line indicates a hypothetical binding mode of a substrate polypeptide chain. Note that the putative catalytic amino-acid residues, D513 in the WWDYG motif, and D571 and K574 in the DK motif, shown in yellow, line both sides of the hydrophobic patch. (B) The overall structure of the full-length STT3, and the location of the three conserved motifs, WWDYG, DK, and DXD. A possible binding mode of a nascent polypeptide chain emerged from a translocon, and that of an oligosaccharide-PP-dolichol/undecaprenol are shown. The aspartate in the WWDYG motif functions as a catalytic base. The DK and DXD motifs are the binding sites for the pyrophosphate group of lipid-linked oligosaccharide donor, through a transiently bound Mn2+ or Mg2+, in a coordinated or sequential manner.