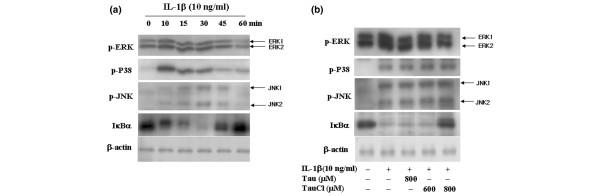
Figure 2.
TauCl primarily inhibited the degradation of IκB. (a) Synovial cells (5 × 105 cells/60 mm dish/2 ml serum-free media) were treated with IL-1β (10 ng/ml). Shown are time courses of the signalling pathways activated during IL-1β stimulation. (b) Synovial cells (5 × 105 cells/60 mm dish/2 ml serum-free media) were treated with taurine chloramine (TauCl) 30 min before 10 or 30 min of IL-1β (10 ng/ml) stimulation for Western blot analysis. A TauCl concentration of 800 μmol/l significantly inhibited the inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (IκB)/nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signalling pathway by inhibiting the degradation of IκBα. The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling pathway, including extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-1/2, p38 and c-jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK), was unaffected. Three independent experiments were performed with cells from two patients. p, phosphorylated.