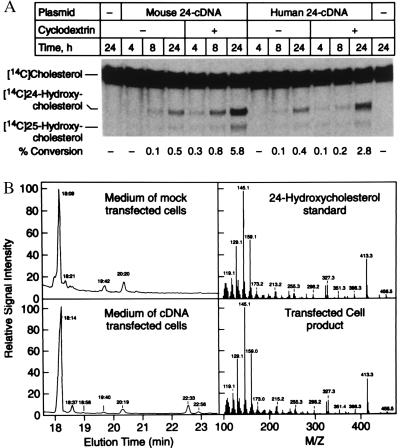
Figure 2.
Expression of cholesterol 24-hydroxylase cDNAs in cultured cells. (A) The indicated expression plasmid was transfected into 293 cells by lipofection. Some cells (+) were treated before substrate addition for 1 h with 20 mg/ml 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin to remove cholesterol from membranes. Thereafter, fresh medium containing radio-labeled substrate was added and the incubation continued for 4, 8, or 24 h. Sterols were extracted from the media and separated by TLC, and the plates were subjected to PhosphorImage analysis to determine the % conversion of substrate into products. A photograph of a typical experiment is shown in the center. Sterol standards are marked on the left. The calculated % conversion for each lane is shown at the bottom. (B) Chemical analyses of 24-hydroxylase products. Cultured 293 cells were transfected with vector alone or a murine 24-hydroxylase expression plasmid (pCMV-m24) as described above except that the posttransfection media was supplemented with 10 μg/ml cholesterol. After 48 h, sterols were extracted from the media, purified by silica chromatography, derivatized to trimethylsilyl ethers, and subjected to GC-MS. (Left) GC profiles of sterols extracted from the media of mock-transfected cells (Upper) or expression vector-transfected cells (Lower). (Right) Ionization spectra of authentic 24R/S-hydroxycholesterol standard (Upper) and the sterol product eluting at 22.33 min from the GC obtained with transfected cell medium (Lower).