FIGURE 10.
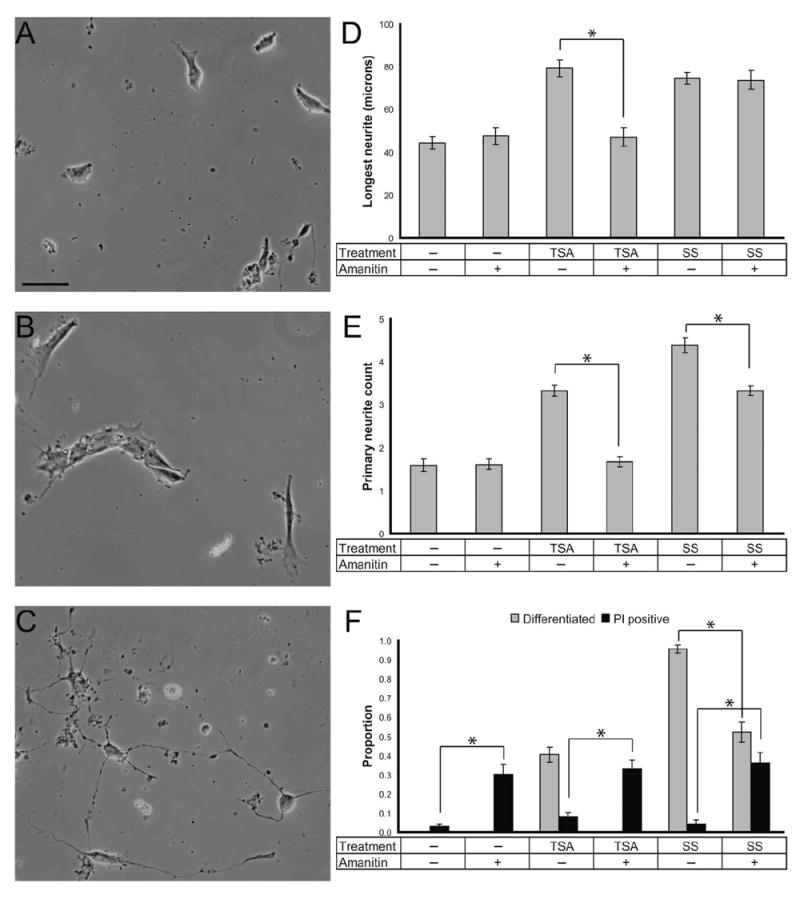
HDAC inhibition–mediated differentiation is transcription dependent. RGC-5 cells were treated with 500 nM TSA and 316 nM SS, with and without the RNA polymerase II inhibitor α-amanitin (10 μg/mL; TSA and SS with α-amanitin (B) and (C), respectively), and were analyzed from photomicrographs taken 24 hours after treatment. HDAC inhibition–mediated differentiated cells were statistically not different from untreated control or α-amanitin–treated control cells (A) in terms of longest neurite length (microns; D), number of neurites longer than the soma (E), and proportion differentiated (F), indicating that transcription is necessary for HDAC inhibition differentiation. These results were not observed with SS differentiation (D–F) because significant neurite outgrowth and differentiation occurred in the presence of α-amanitin. *Statistically significant (P < 0.05) difference between treatments. Scale bar, 50 μm.
