FIGURE 6.
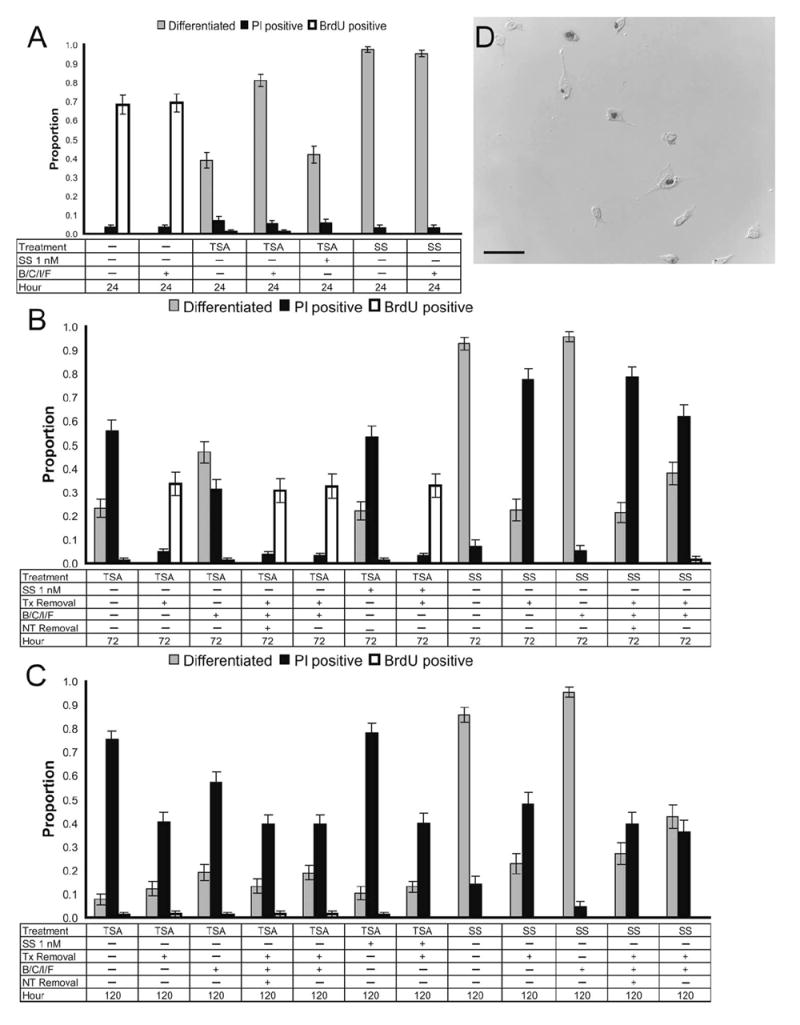
HDAC inhibition–differentiated RGC-5 cells are postmitotic. RGC-5 cells were treated with 500 nM TSA or 316 nM SS with or without RGC survival factors (B/C/I/F) or a subthreshold dose of SS (1 nM). Cells were maintained in their initial treatment conditions, and photomicrographs were taken 24 hours (A) after treatment. Alternatively, various combinations of the differentiation-inducing drugs and neurotrophic factors (NT; i.e., B/C/I/F) were removed at 24 and 72 hours, with photomicrographs taken 48 hours later, at 72 (B) and 120 hours (C), respectively. These conditions were performed simultaneously in 24-well plates. BrdU (100 μM) was administered 4 hours before the end of the test period, and immunohistochemical staining was performed for incorporation into chromatin to examine the mitotic state of cells. Although untreated control cells were mitotically active at 24 hours (A, D; 68% ± 5% BrdU positive), cells differentiated with TSA or staurosporine were observed to be mitotically inactive, with less than 2% BrdU positive at all time points (A–C). The exception was when TSA was removed at 24 hours, with at least 31% of cells becoming BrdU positive regardless of maintenance in neurotrophic factors (B). This indicated that HDAC inhibition for 24 to 72 hours is necessary for these cells to become irreversibly postmitotic.
