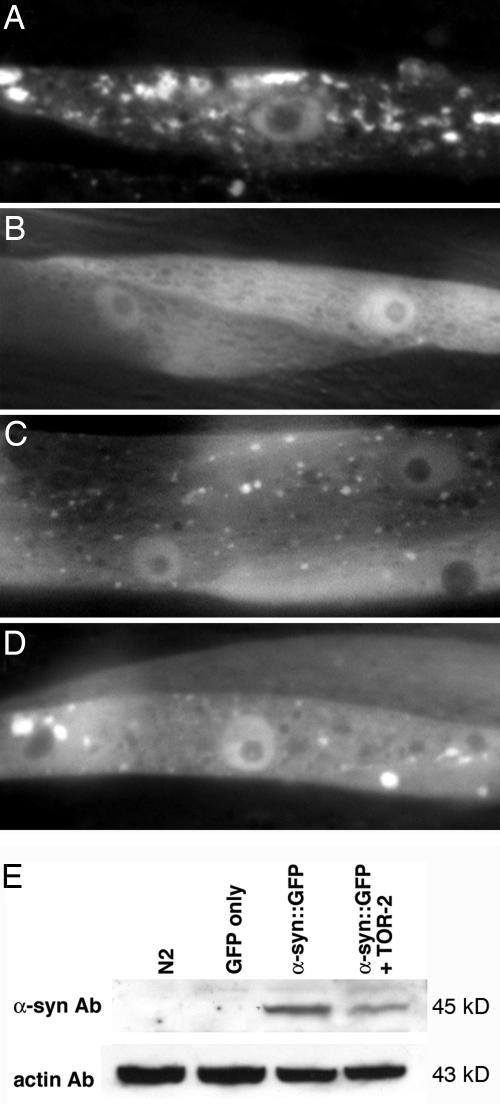
Fig. 1.
RNAi knockdown of specific gene targets enhances misfolding of α-syn. (A) Isogenic worm strain expressing α-syn::GFP alone in body wall muscle cells of C. elegans. (B) The presence of TOR-2, a protein with chaperone activity, attenuates the misfolded α-syn protein. (C and D) When worms expressing α-syn::GFP and TOR-2 are exposed to candidate gene RNAi, the misfolded α-syn::GFP returns. (E) Western blot analysis of α-syn::GFP demonstrating the presence of α-syn::GFP in worms with and without TOR-2 coexpression. Actin was used as a loading control.