Fig. 2.
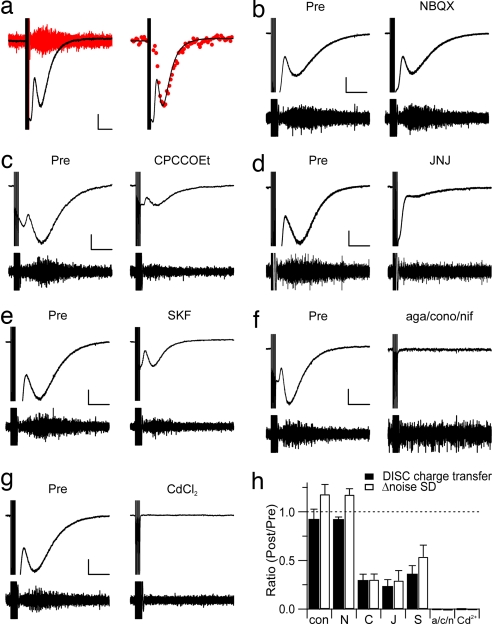
DISC is Ca2+-triggered and involves activation of mGluR1 and TrpC1 cation channels. (a Left) When single-exemplar current traces were high-pass-filtered at 10 Hz, this revealed a significant increase in noise at the peak of DISC (red). [Calibration bars: 100 pA, 2 sec (current trace); 10 pA, 0.2 sec (filtered trace).] (Right) The standard deviation was calculated from 200-msec-long segments of the high-pass-filtered traces to yield the noise SD. Noise SD values from five sequential episodes (red circles) were scaled and superimposed on the current trace, which is an average of the same five episodes. (b–g) Both current and the high-pass-filtered traces were plotted before and after application of various receptor antagonists or channel blockers (100 μM NBQX; 100 μM CPCCOEt; 50 μM JNJ 16259685; 30 μM SKF 96365; a mixture of 0.2 μM ω-agatoxin IVA, 3 μM ω-conotoxin MVIIC, and 3 μM nifedipine; or 250 μM Cd2+). [Calibration bars: 200 pA, 2 sec (current traces).] The high-pass-filtered traces are displayed by using a range of −25 to 25 pA. (h) The averages of either DISC charge transfer (filled bars) or Δ noise SD (open bars) are plotted as a ratio of measurements 20 min after drug application to a preexposure baseline (con, control; N, NBQX; C, CPCCOEt; J, JNJ 16259685; S, SKF96365; a/c/n: mixture of Ca2+ channel blockers).