Figure 2.
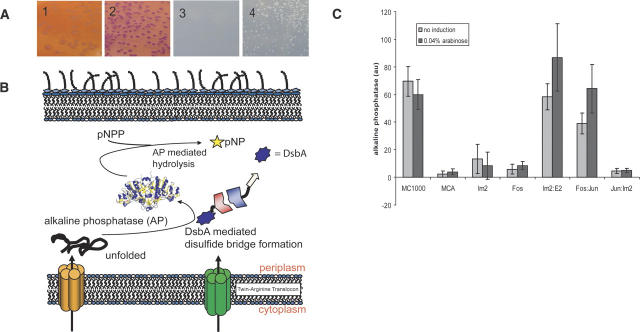
Detection of interacting proteins via Tat two-hybrid using MalE or DsbA as reporters. (A) Use of MalE as a reporter. (1) E. coli HS3018 (malE−) cells coexpressing ssTorA(KK)-wbJun fusion with a nonfunctional Tat signal peptide (from pEMS16) and wbFos-MBP (from pEMS11) grown on MacConkey plates with 0.4% maltose; (2) E. coli HS3018 (malE−) coexpressing ssTorA-wbJun (pEMS12) with wbFos-MBP (pEMS11) grown on MacConkey plates with 0.4% maltose; (3) cells as in panel 1 plated on M9 media with 0.4% maltose and incubated for 4 d at 37°C; (4) Cells as in panel 2 grown on maltose minimal media plates as in panel 3. (B) Detection of protein:protein interactions by an enzymatic assay using DsbA as a reporter: Interaction of the prey–ΔssDsbA fusion with ssTorA–bait results in the formation of a complex that is translocated into the periplasm by the Tat pathway via the ssTorA signal peptide. In the periplasm, DsbA catalyzes the oxidative folding of AP, the activity of which can be detected using the chromogenic substrate pNPP. (C) Alkaline phosphatase activity in arbitrary units (au). Cells were grown in MOPS low-phosphate media with or without 0.04% arabinose, harvested after 6 h, and the AP activity was measured as described in the Materials and Methods. (MC1000) E. coli positive control; (MCA) MC1000 ΔdsbA∷kan, negative control; (Im2) E. coli MCA expressing ΔssDsbA-Im2 from pEMS14; (Fos) MCA expressing wbFos-ΔssDsbA from pEMS13; (Im2:E2) coexpression of the ΔssDsbA-immunity protein 2 fusion from pEMS14 together with the ssTorA-endonuclease domain of colicin E2 (H575A) fusion from pEMS15; (Fos:Jun) coexpression of ssTorA-wbJun from pEMS12 with the wbFos-ΔssDsbA fusion (pEMS13); (Jun:Im2) coexpression of ssTorA-Jun from pEMS12 with immunity protein2 fused to ΔssDsbA (pEMS14).