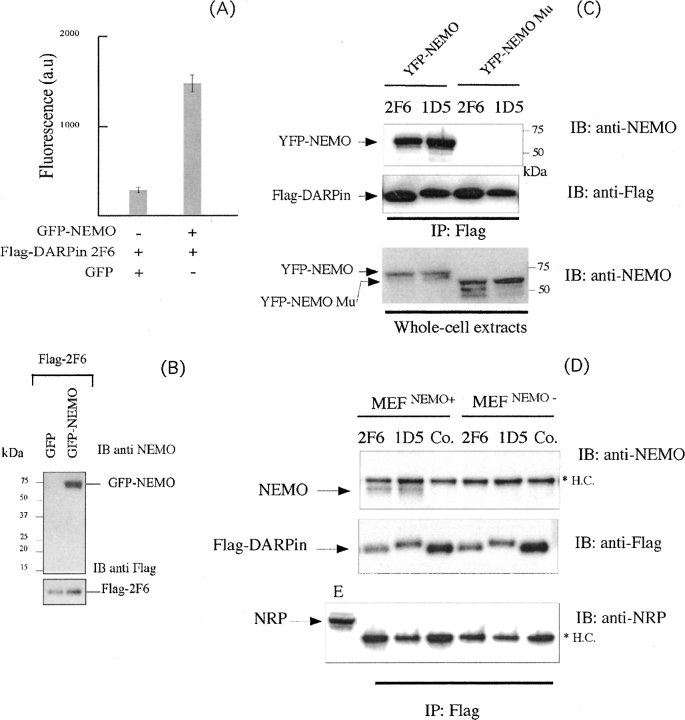
Figure 5.
NF-κB inhibition by DARPin occurs through the specific interaction with NEMO. (A,B) Specific binding of 2F6 to GFP-NEMO. 293 HEK cells were transfected with the indicated expression vectors. After 24 h, cell lysates were prepared and an anti-Flag immunopurification experiment was performed using anti-Flag antibody prior to the elution by Flag peptide. The peptide eluate was then analyzed by (A) fluorescence at 535 nm or by (B) immunoblot with anti-NEMO antibodies. For the immunoblot, equivalent amounts of input (one-fourth of the eluates) were loaded on each lane of the SDS-PAGE gel. (C) 2F6 and 1D5 bind to YFP-NEMO through the specific recognition of the CC2-LZ domain. An experiment similar to that described for B was performed after transient transfection of 293 HEK cells with the indicated Flag-DARPins in combination with YFP-NEMO or YFP-NEMO deleted of the CC2-LZ domain (YFP-NEMO Mu). (IB) Immunoblot; (IP) immunoprecipitate. (D) 2F6 and 1D5 specifically bind to the endogenous NEMO. The indicated Flag-DARPins or the Flag naive DARPin (Co.) were individually immunopurified after transient expression in 293 HEK cells as described in A. The eluted DARPins were then incubated with crude extracts prepared from MEFs or NEMO-deficient MEFs, and a second anti-Flag immunoprecipitation experiment was performed. The resulting protein complexes were subjected to an immunoblot (IB) analysis using the indicated antibodies. (HC) Heavy chain antibody; (E) whole-cell extracts.