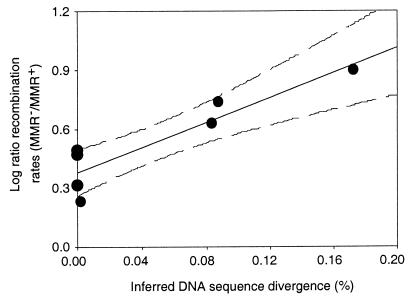
Figure 4.
Inhibition of recombination because of MMR increases with inferred sequence divergence. The inferred divergence between each of the donor–recipient pairs in Fig. 2 was calculated by using a neutral model of evolution, assuming a mutation rate of 5 × 10−10 per base pair per generation (27) for nonmutators and a 100-fold higher rate for mutators. For example, A−2 diverged from the ancestor for 2,400 generations at the nonmutator rate and 17,600 generations at the mutator rate. The inferred divergence is 1 − (1 − 5 × 10−10)2400 × (1 − 5 × 10−8)17,600 = 0.00088 = 0.088%. The line is the regression of the log-transformed ratio of recombination rates for isogenic MMR− and MMR+ recipients crossed with the same donor vs. the inferred sequence divergence between donor and recipient (r = 0.9132, n = 7, P = 0.0041). The dashed curves show 95% confidence interval around the regression.