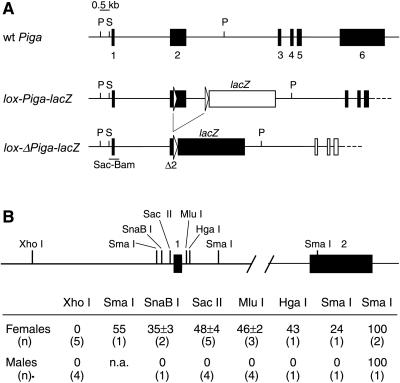
Figure 1.
(A) Genomic structure of wt Piga, lox-Piga-lacZ, and lox-Piga-lacZ after recombination (lox-ΔPiga-lacZ). Two loxP sites (open arrows) and the coding region for lacZ (lacZ-box) were introduced into the Piga locus by homologous recombination in murine ES cells (12). In the lox-Piga-lacZ configuration, PIGA function is not impaired (filled boxes), and LacZ is not expressed (open lacZ box). However, after Cre-mediated excision of the DNA sequences between the two lox sites Piga becomes inactivate (open Piga boxes) and LacZ falls under the endogenous Piga promoter and is expressed (filled lacZ box). Restriction sites used in the methylation assay are shown. P, PstI; S, SacII. Genomic DNA was digested with PstI (P) to obtain restriction fragments suitable for Southern blotting. Each PstI fragment has a different size depending on whether it is derived from the wt (7.0 kb), the lox-Piga-lacZ (10.4 kb), or the lox-ΔPiga-lacZ (8.1 kb) gene. To determine the extent of methylation DNA was subsequently digested with the methylation-sensitive restriction endonuclease SacII (S). If the 5′ SacII site is unmethylated, each fragment is shortened by 0.5 kb. The Sac-Bam DNA probe used for hybridization is shown. (B) The diagram shows the promoter region and intron 1 of the Piga gene with the endonuclease cleavage sites that are subject to methylation depending on the inactivation status of the gene. Lower shows the proportions of DNA that is methylated in wt mice. Values were defined by the use of a phosphoimager (see Materials and Methods) and are shown as the mean and SD of all measured samples. n.a., not analyzed.