Diagram 1. Functional association of mtNOS with RCC-I.
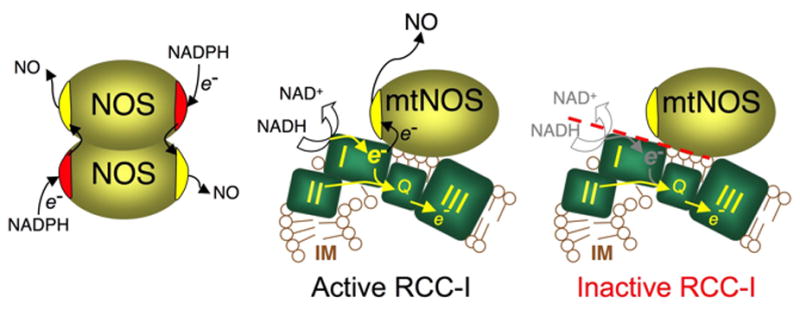
Cytoplasmic NOS isozymes consist of a reductase and an oxygenase domain. Each monomer homodimerizes in a configuration that allows electrons flow from the reductase domain of one monomer to the oxygenase domain of the coupling monomer where NO is produced. mtNOS that is localized at mitochondrial inner membrane (IM) where respiratory chain complexes are located. Electrons enter the chain from respiratory complex I (I) or RCC-II (II) and flow down to ubiquinone (Q) and downstream complexes (only RCC-III is shown). mtNOS functionally associates with RCC-I and utilizes RCC-I as source of electrons. When RCC-I is active, mtNOS receives electrons enabling the enzyme to produces NO. Inactivation of RCC-I ceases mtNOS reducing equivalents and abolishes its NOS activity.
