Figure 2. Soluble hemojuvelin release from the hemojuvelin-alkaline phosphatase chimera protein is sensitive to furin convertase inhibitor (FCI) and iron loading.
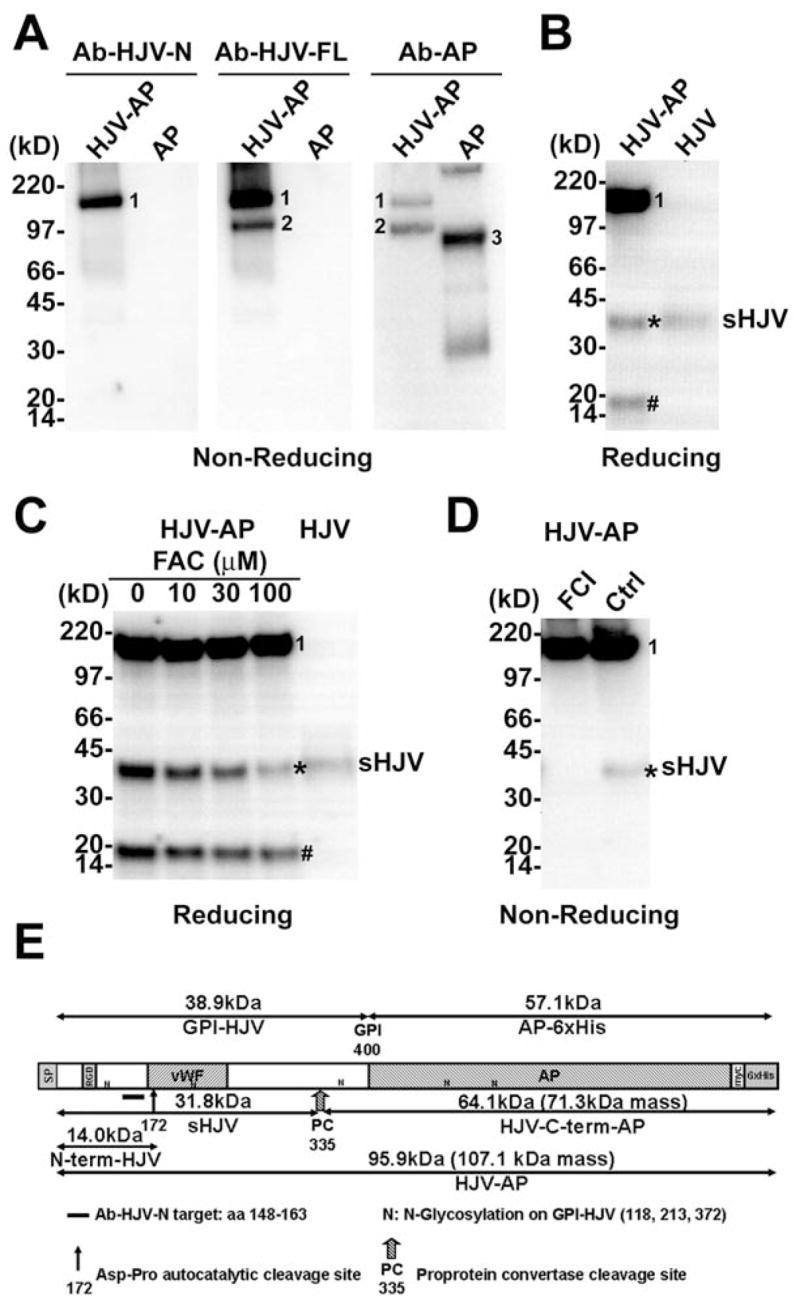
(A) Conditioned cell culture media from pHJV-AP and pAP HEK293 stable cell cultures were purified using a nickel-column, and analyzed on a non-reducing SDS-PAGE. Western blot was probed with Ab-HJV-N, Ab-HJV-FL and Ab-AP antibodies. (B) Conditioned cell culture media from pHJV-AP and pHJV HEK293 stable cell cultures were analyzed on a reducing SDS-PAGE. Western blot was probed with Ab-HJV-N antibody. (C) pHJV-AP HEK293 stable cell cultures treated with ferric ammonium citrate (FAC) at 0, 10, 30 and 100 μM. Conditioned cell culture media were analyzed on a reducing SDS-PAGE. Western blot was probed with Ab-HJV-N antibody. (D) pHJV-AP HEK293 stable cell cultures treated with or without 25 μM furin convertase inhibitor (FCI). Conditioned cell culture media were analyzed on a non-reducing SDS-PAGE. Western blot was probed with Ab-HJV-N antibody. (E) Schematic illustration of human hemojuvelin ectodomain (aa 36-400)-alkaline phosphatase chimera protein (HJV-AP). SP: signal peptide (aa 1-35); RGD: RGD motif (aa 98-100); vWF: partial von Willebrand factor domain (aa 167-253). Visible bands correspond to mature full-length hemojuvelin-alkaline phosphatase chimera protein (band 1), HJV-C-term-AP fragment (band 2), human alkaline phosphatase (band 3), s-hemojuvelin produced by pHJV-AP HEK293 cells (sHJV, *) and the N-terminal fragment of hemojuvelin-alkaline phosphatase (N-term-HJV, #).
