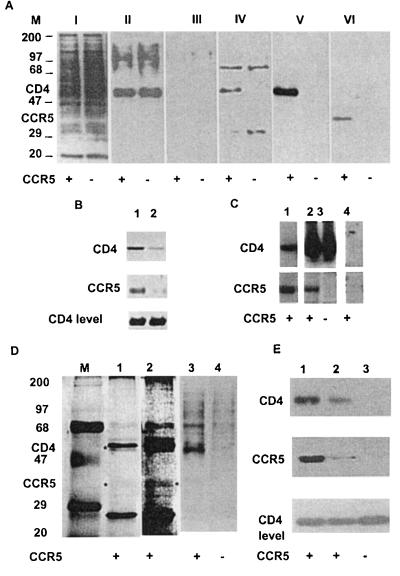
Figure 1.
Specific coimmunoprecipitation of cell surface-associated CD4 and CCR5 from 3T3 cells coexpressing these two molecules. (A) Equal numbers of 3T3 cells expressing CD4 and CCR5 (+) or CD4 only (−) were biotinylated, processed as described in Materials and Methods, and either used as a whole-cell lysate (0.25% of total, gel I) or immunoprecipitated with an anti-CD4 mAb (OKT4) (gel II), anti-CXCR4 mAb (4G10) (gel III), or anti-CCR5 mAb 5C7 (gels IV–VI). The biotinylated proteins were detected by using streptavidin–horseradish peroxidase (gels I-IV). CD4 and CCR5 were detected in an aliquot of the same samples as in gel IV by using Western blotting with an anti-CD4 polyclonal antibody (T4-4) (gel V) or an anti-CCR5 polyclonal antibody [CKR5(C20)] (gel VI). (M denotes molecular markers, and the numbers are in kDa). (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of CD4 by the anti-CCR5 mAbs m180 (lane 1) and m181 (lane 2). The coimmunoprecipitated CD4 and the immunoprecipitated CCR5 were detected by sing Western blotting as in A. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of CCR5 from 3T3.CD4.CCR5 cells with anti-CD4 antibodies. 3T3.CD4.CCR5 cells (lanes 1, 2, and 4) or 3T3.CD4 cells (lane 3) were used for immunoprecipitation by OKT4 (lanes 2 and 3) or by a control antibody (CG10) (lane 4). Lane 1 shows for comparison immunoprecipitation with the anti-CCR5 mAb 5C7. CD4 and CCR5 were detected by using Western blotting as in A. (D) Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated by the anti-CCR5 mAb 5C7, the immunoprecipitation product was analyzed by using a silver stain kit (lanes 1 and 2) and compared with proteins detected by streptavidin–horseradish peroxidase in biotinylated lysates (lanes 3 and 4). M denotes molecular weight marker, and + and − denote 3T3.CD4.CCR5 or 3T3.CD4 cells, respectively. ∗, bands caused by CD4 and CCR5. The two bands above and below CD4 are caused by the 5C7 mAb heavy and light chain, respectively. Lane 2 represents lane 1 at higher sensitivity, where CCR5 is clearly seen. (E) CD4–CCR5 coimmunoprecipitation is not significantly affected by cholesterol depletion. 3T3.CD4.CCR5 cells were treated with 10 mM methyl-β-cyclodextrin for 1 hr at 37°C (which caused significant cytotoxicity) and used for immunoprecipitation by the anti-CCR5 antibody 5C7 (lane 2), and compared with untreated cells (lane 1) and 3T3.CD4 cells (lane 3). CD4 and CCR5 were detected by using Western blotting as in A. Bottom shows Western blotting of CD4 from whole-cell lysates.