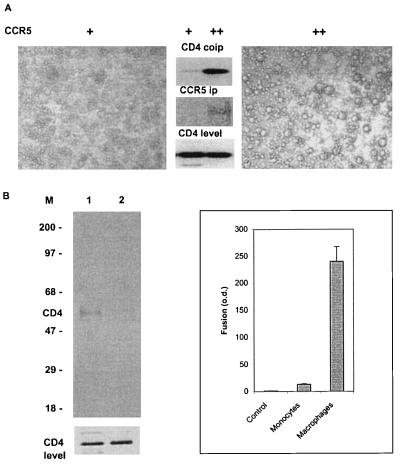
Figure 2.
Coimmunoprecipitation of CD4 and CCR5 in primary cells. (A) Human CD4 T cells expressing high (+) and very high (++) amounts of CCR5 were used for immunoprecipitation with the anti-CCR5 mAb 5C7 (Center) or fusion with HeLa cells expressing the HIV-1 JRFL Env (Left and Right). The coimmunoprecipitated CD4 (Center Top) and immunoprecipitated CCR5 (Center Middle) were detected by using Western blotting as in Fig. 1A. The CD4 Western blotting of whole-cell lysates is shown (Bottom) as a measure of the level of CD4. The average number of syncytia for ++ cells was 92 ± 10.5, for + cells was 29 ± 7, and for control HeLa cells was 6 ± 3. The average diameter of syncytia from the ++ cells was about 4-fold larger than that for the + cells. (B) Human macrophages (Left, lane 1) and monocytes (Left, lane 2) were used for CCR5 immunoprecipitation. CD4 coimmunoprecipitation was detected as in A. The CD4 Western blotting of whole-cell lysates is shown (Bottom) as a measure of the level of CD4. (Right) Fusion of these cells with HeLa cells expressing the HIV-1 JRFL Env as quantitated by the β-galactosidase assay. The control represents HeLa cells that do not express HIV-1 Env.