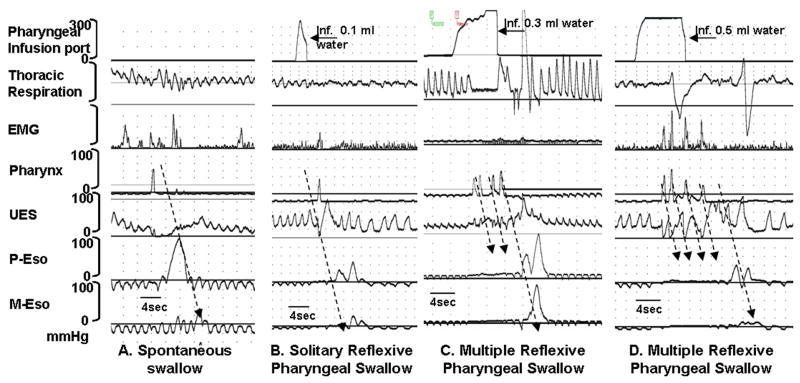
Figure 3.
Examples of A) spontaneous swallow, B) solitary PRS, and C and D) multiple swallow sequences. Each swallow is associated with submental EMG signal and UES relaxation. Recordings from P-Eso, M-Eso and D-Eso represent proximal-, middle-, and distal esophageal motility respectively. In figures A and B, note the propagation of peristaltic waveforms with solitary swallows. In figures C and D, multiple succeeding swallows inhibit the propagation of previous swallow. Only the terminal pharyngeal swallow resulted in a fully propagated sequence.