Fig. 1.
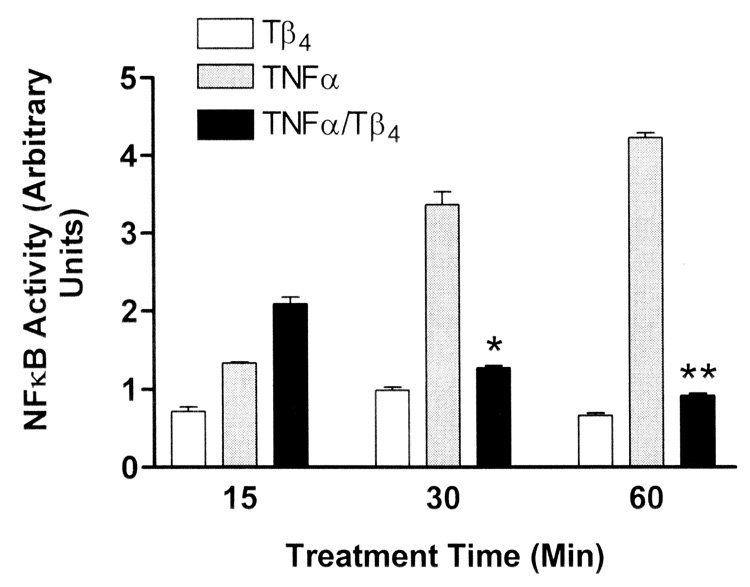
Tβ4 suppresses NFκB activity in human corneal epithelial cells in vitro. Transformed human corneal epithelial cells (HCET) were treated with 1 µg/ml Tβ4 only (open bars) or stimulated with 10 ng/ml TNF-α (gray bars) only. HCET were also stimulated with TNF-α and simultaneously treated with Tβ4 (black bars) for the times indicated. At assay times less than 20 min, Tβ4 treatment resulted in increased NFκB activity in TNF-α stimulated cells (only the 15 min data is shown). In contrast by 30 min of Tβ4 treatment, NFκB activity was significantly suppressed in TNF-α stimulated cells (* P = 0.0068, ** P < 0.0001). Note that NFκB activity in HCET treated with Tβ4 alone is consistently lower than in cells treated with TNF-α. NFκB activity in media control cells was negligible and is not shown.
