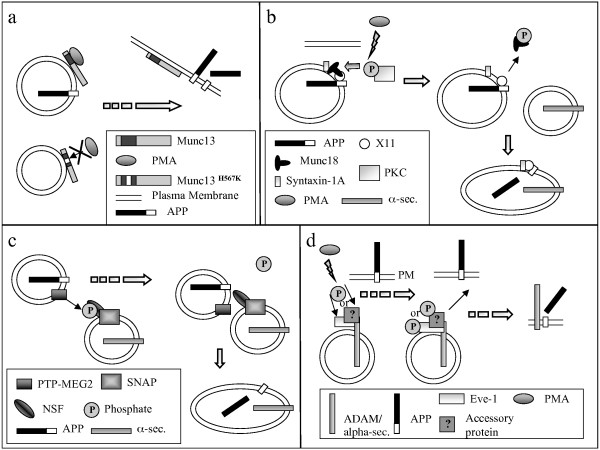
Figure 6.
Possible mechanisms for how the PMES candidates tested in this study might modulate shedding of the APP ectodomain. a, This cartoon depicts how phorbol esters (PMA) might promote translocation of wildtype but not H567K Munc13-1 to the PM. b, This cartoon depicts how phosphorylation of Munc18 by PKC might facilitate fusion of APP transport vesicles with α-secretase transport vesicles, thereby facilitating shedding. c, This cartoon depicts how dephosphorylation of phospho-NSF might disinhibit NSF-mediated vesicle fusion; as in b, the notion is that APP and α-secretase might be traveling in separate vesicles prior to phosphorylation-state mediated facilitation of vesicle fusion. d, This cartoon depicts how the phosphorylation state of Eve-1 (or some theoretical accessory Eve-1 binding protein) might modulate vesicle interactions with the PM or they might modulate the physical docking between APP and α-secretase.