Figure 1. Generation and analysis of v7−3 knockout mice.
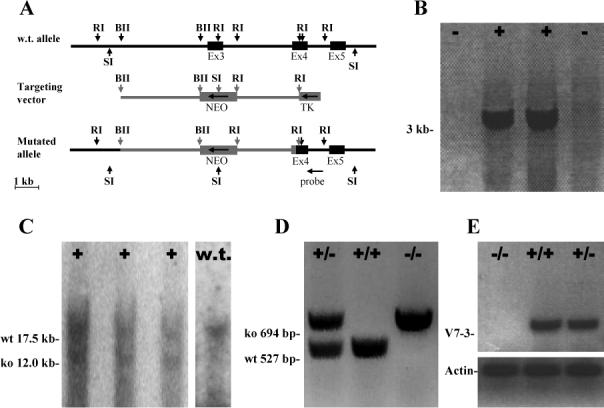
(A) Genomic organization of the v7−3 gene (black) and the gene targeting construct (gray). Full boxes represent exons and arrow heads important restriction sites: RI, EcoRI; BII, Bgl II, SI, Sac I. Direction of transcription for Neo is opposite to that of v7−3 as indicated by the arrow. (B) Two positive and two negative ES cell clones screened by PCR with primers J5 and J8. (C) Southern blot analysis of the clones positive by PCR. SacI digestion produced a 17.5 kb fragment from the wild type allele, and a 12.0 kb fragment from the mutated allele because the Neo cassette introduced a new SacI site. (D) PCR genotyping of v7−3 mice. (E) RT-PCR analysis of brain expression of the v7−3 (primers J52, J53) and actin (ACTf, ACTr) in wild type and mutant mice.
