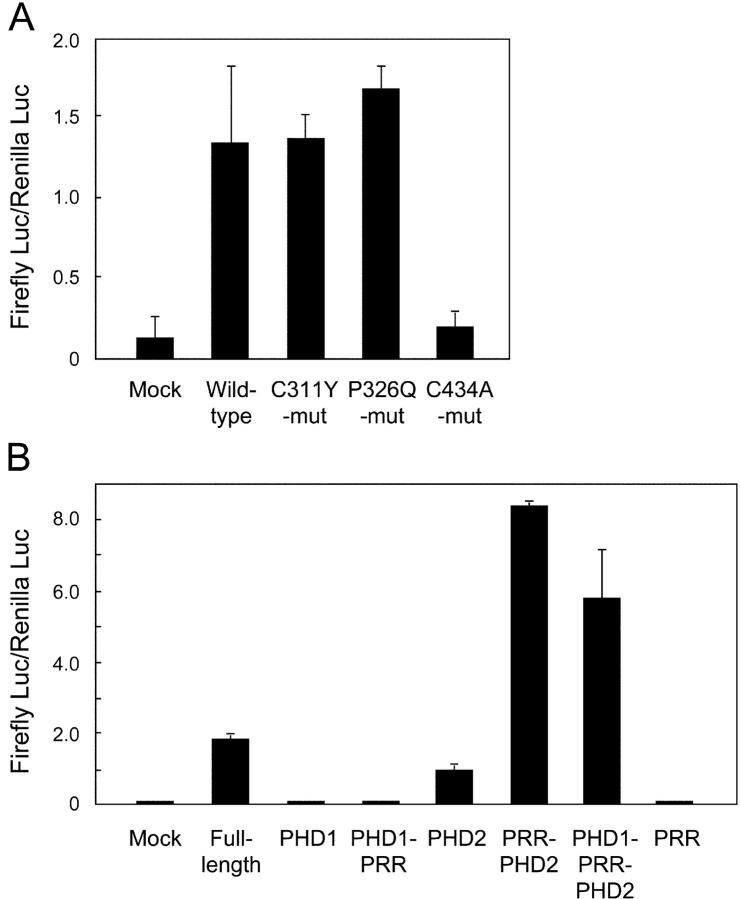
Figure 3.
Effect of PHD mutations on the transcriptional transactivating properties of AIRE. (A) Various forms of full-length AIRE including disease-causing mutations were fused with Gal4-binding domain and transfected into mTEC cells together with a reporter plasmid. Firefly luciferase activities were normalized with respect to the Renilla luciferase activities used for assessment of the transfection efficiency. No significant reduction of Gal4 activation was observed from the disease-causing mutations of PHD1 (C311Y and P326Q), whereas the PHD2 mutant (C434A) showed loss of transcriptional activation. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM for triplicate wells during one representative experiment from a total of five repeat experiments. (B) Isolated PHDs were tested for the transcriptional activation with the same system described in A. The fragments used are as follows (see Figs. 1 A and 2 A): PHD1, amino acids 292–341; PHD1 plus PRR, 292–432; PHD2, 433–545; PRR plus PHD2, 342–545; PHD1 plus PRR plus PHD2, 292–545; and PRR, 342–432. PHD2 suffices for the transcriptional activation in this assay, whereas PHD1 has no such activities. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM for triplicate wells during one representative experiment from a total of three repeat experiments.