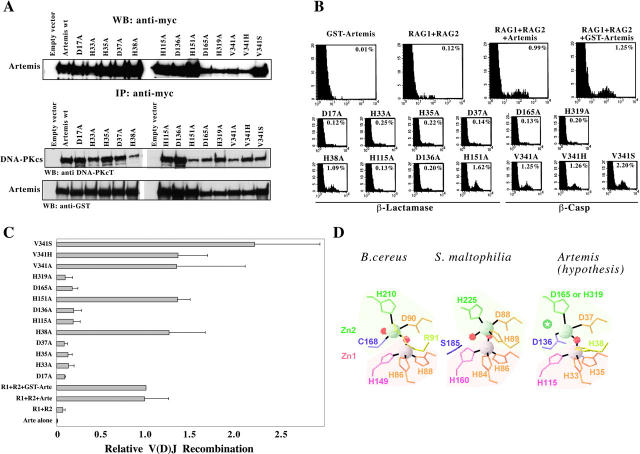
Figure 4.
V(D)J recombinase activity of in vitro–generated Artemis mutants. (A) All mutants are expressed in 293T cells and retain their capacity to interact with DNA-PKcs. (B) FACS® analysis of GUETEL/RSS cells transiently transfected with RAG1, RAG2, and the various Artemis mutants. The percent of recombination refers to the frequency of EGFP+ cells among the CD4+ cells. (C) Integrated results of four experiments showing the relative V(D)J recombination activity of the mutants relative to the recombination frequency using GST-Arte. (D) Hypothetical model for the structure of the catalytic site of Artemis. This model is based on the structure of the B. cereus and S. maltophilia β-Lacts as adapted from Wang et al. (reference 14; PDB codes: 1BC2 and 1SML, respectively). Gray and red spheres indicate the position of zinc and water oxygen atoms, respectively. Shaded areas correspond to the two Zn(II)-binding domains. The green star indicates the position of the fifth Zn2 ligand, which may correspond to a water molecule, or to a conserved amino acid of the β-CASP region (possibly D165).