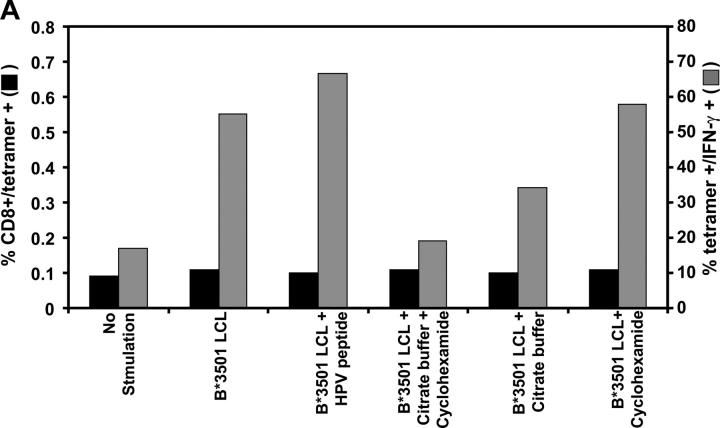
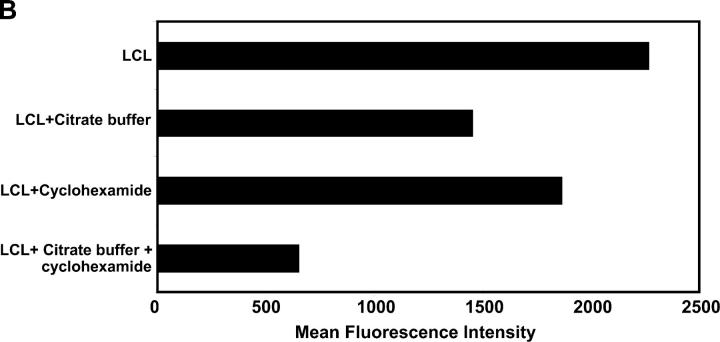
Figure 8.
(A) Effect of MHC–peptide stripping and cycloheximide treatment on ex vivo intracellular IFN-γ production by EBNA1-specific T cells. PBMCs from an HLA B35+ donor were incubated alone or with either an HLA B*3501+ LCL, an HLA B*3501+ LCL plus 0.01 μM HPV peptide, an HLA B*3501+ LCL treated with citrate buffer and 50 μM cycloheximide, an HLA B*3501+ LCL treated with citrate buffer, or an HLA LHLA B*3501+ LCL treated with cycloheximide. Data shown represents the CD8+ and tetramer+ population (solid bars) and the tetramer+ population producing IFN-γ (shaded bars). This data is a representation of two separate experiments. (B) Surface MHC class I expression on untreated LCLs or LCLs treated with either cycloheximide, citrate buffer alone, or cycloheximide and citrate buffer. LCLs were initially incubated with MHC class I–specific mAb (W6/32) followed by incubation with FITC-labeled anti–mouse Ig. The fluorescence intensity was measured by FACSCalibur™ and data were analyzed by CELLQuest™ software. The results are expressed as mean fluorescence intensity.