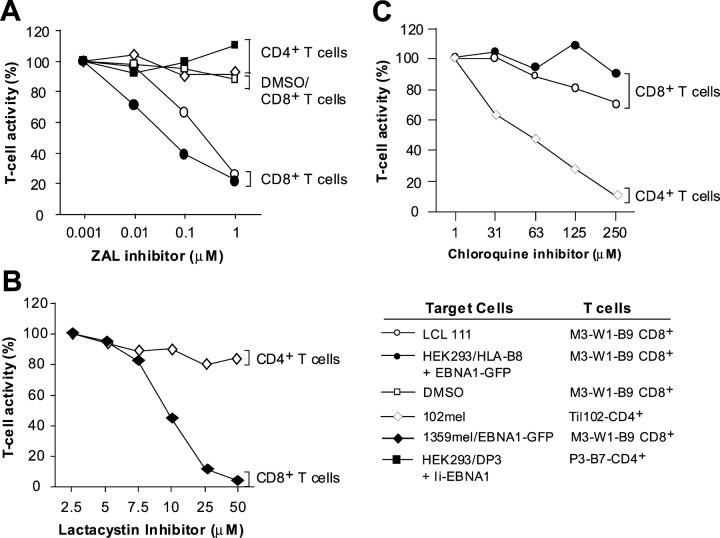
Figure 8.
Specific inhibition of T cell recognition of EBNA1 by proteasomes inhibitors. (A) Blocking of T cell recognition of EBNA1 by a ZAL proteasome inhibitor. HEK 293 cells cotransfected with EBNA1-GFP were treated with various concentrations of ZAL inhibitor for 10 h. After washing, cells were incubated with T cells overnight for IFN-γ release assays. Various dilutions of DMSO were used as controls. T cell activity in the absence of inhibitor was used at 100% activity. Two CD4+ T cells were used to demonstrate the specificity of ZAL inhibitor. TIL102 and P3-B7 CD4+ T cells able to recognize 102mel and HEK293/DP3/Ii-EBNA1 target cells, respectively, were not inhibited by ZAL. (B) Inhibition of M3-W1-B9 CD8+ T cell recognition of 1359mel target cells stably expressing EBNA1-GFP by lactacystin proteasome inhibitor. The lactacystin inhibitor did not affect recognition of 102mel tumor cells by TIL102 CD4+ cells. (C) Blocking of MHC class II antigen processing by chloroquine. Inhibition of T cell recognition of 102mel cells by TIL102 CD4+ was observed after treatment with chloroquine in a dose-dependent fashion. By contrast, T cell recognition of LCL 111 and HEK293 transfected with HLA-B8 and EBNA1-GFP cDNAs was not significantly affected after the treatment of chloroquine.