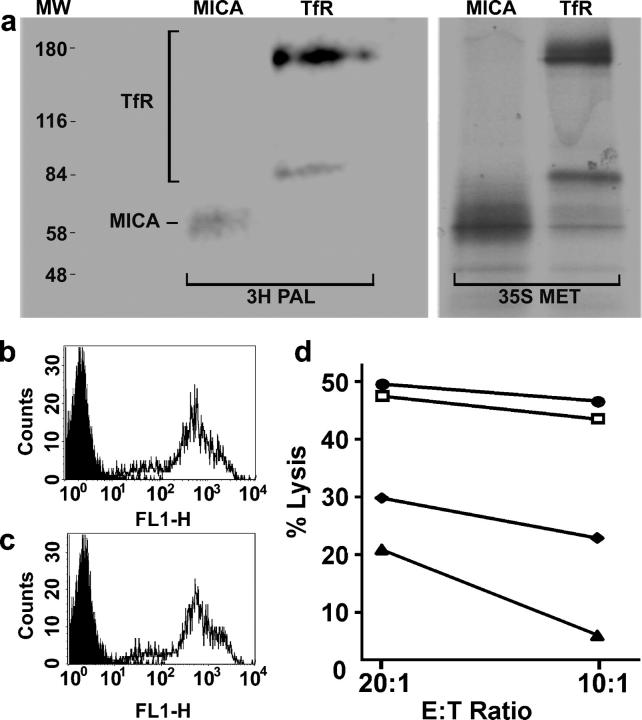
Figure 4.
MICA is S-acylated, and a truncated form of MICA is unable to activate NK cells. (a) Daudi/Class I+/MICA cells were labeled for 5 h with either [35S]methionine (35S MET) or with [3H]palmitate (3H PAL), lysed, immunoprecipitated with anti-MICA or anti-TfR mAb, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and fluorography. Molecular weight markers (MW) are also shown. The two bands seen for TfR correspond to the size of TfR monomers and dimers. The mobility of MICA was higher in this gel than in that used in Fig. 2, probably due to the nonreducing conditions. Fluorograms were exposed for 81 d (3H PAL) or 7 d (35S MET). (b and c) Cell surface staining by anti-MICA mAb of (b) Daudi/Class I+/MICA and (c) Daudi/Class I+/MICA/C331*. Plots show staining with an isotype-matched control mAb (shaded) and staining with anti-MICA (line). (d) Susceptibility of Daudi (□), Daudi/Class I+ (♦), Daudi/Class I+/MICA (•), and Daudi/Class I+/MICA/C331* (▴) by a peripheral blood NK cell line, assessed in a 5-h [35S]Met release assay. Data are representative of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate.