Figure 6.
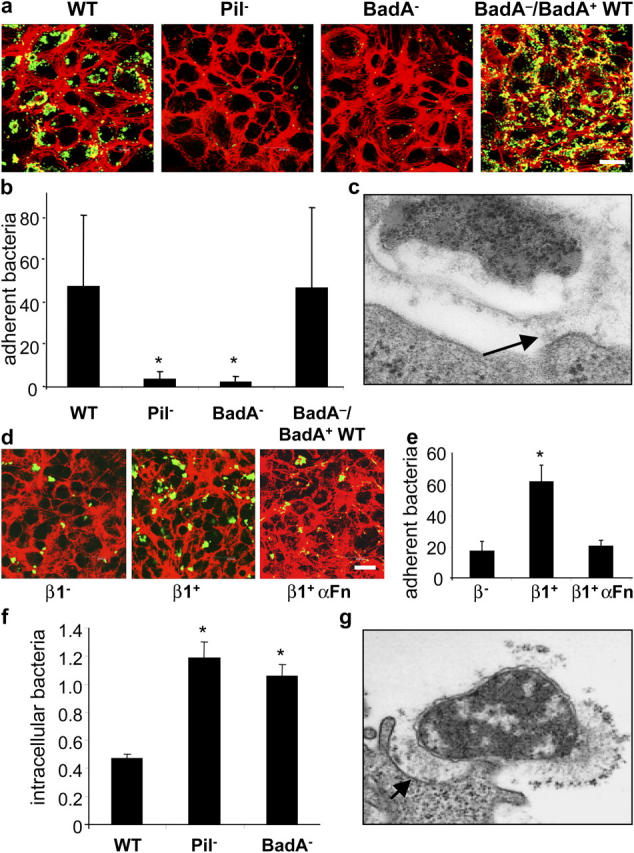
BadA mediates cell adherence and shares antiphagocytic properties. (a) Adherence of B. henselae WT, Pil−, BadA−, and BadA−/BadA+ WT to ECs shown by CLSM. Bacteria were labeled by FITC-conjugated antibodies (green signal) and filamentous actin was stained with TRITC-labeled phalloidin (red signal). Bar, 20 μm. (b) Microscopic quantification (bacteria/cell) of EC adherence. (c) Adherence of B. henselae WT to ECs shown by TEM. Note that adherence of B. henselae WT to the cell surface is mediated via BadA (arrow). (d) Adherence of B. henselae WT to GD25 (β1−) and GD25 β1 integrin–overexpressing (β1+) fibroblasts shown by CLSM. For modulation, bacteria and β1+ cells were preincubated with anti-Fn antibodies (β1+ αFN). (e) Microscopic quantification of bacterial adherence to GD25 and GD25 β1 integrin+ fibroblasts. (f) Intracellular B. henselae WT, Pil−, and BadA− 3 h after infection of J774 macrophages. Bacteria (percent of inoculum) were calculated from gentamicin protection assays. (g) Interaction of B. henselae WT with J774 macrophages shown by TEM. Note that adherence of B. henselae WT to the cell surface is mediated via BadA (arrow). *, Significant difference compared with B. henselae WT (P < 0.01).
