Figure 2.
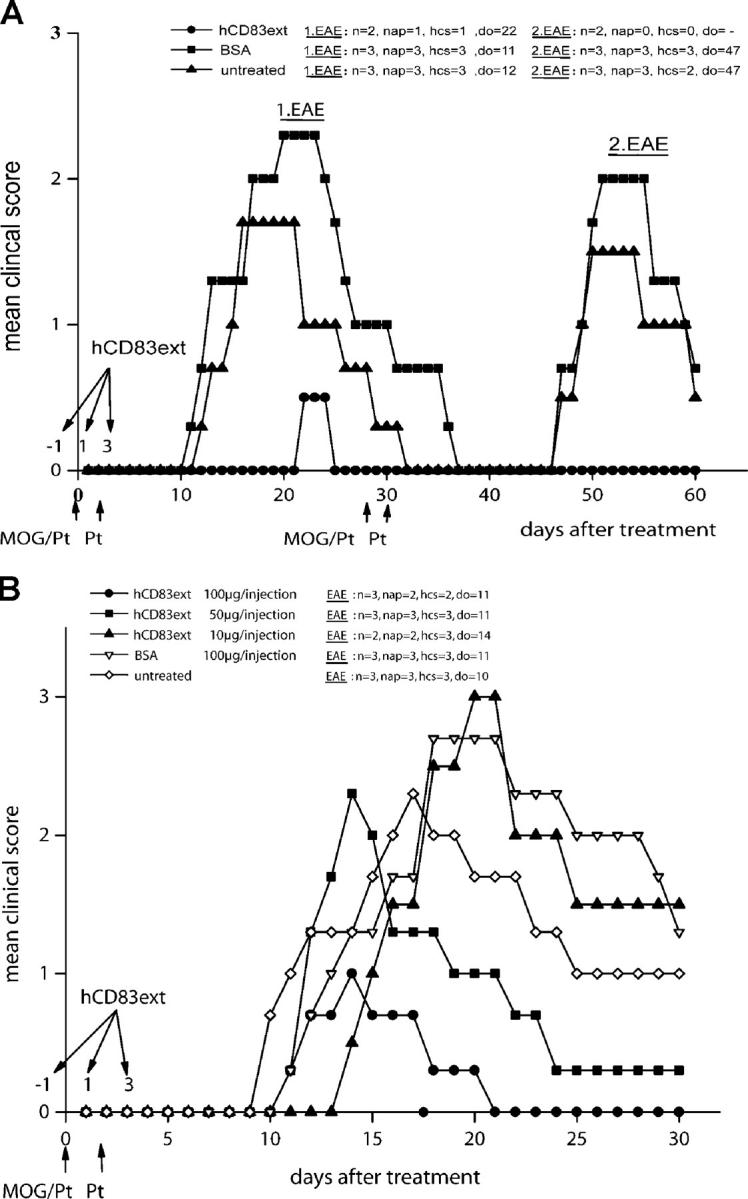
Three doses of soluble CD83 protect mice from EAE. (A, left) 100 μg hCD83ext (or BSA as control) were injected i.p. on days −1, 1, and 3. EAE was induced by s.c. injection of MOG peptide emulsified in CFA enriched with M. tuberculosis at day 0 as described in Materials and Methods. In addition, 200 ng Pt was administered i.p. on days 0 and 2. hCD83ext almost completely inhibited the paralysis. In contrast, BSA-treated and untreated mice developed strong disease symptoms. (A, right) On day 28, EAE was induced a second time by immunizing the mice with MOG peptide as described above. Strikingly, mice which were treated only three times with hCD83ext were completely protected, whereas untreated and BSA-treated mice were paralyzed. (B) Inhibitory effect is dose dependent. hCD83ext was administered at three different doses. The best inhibition was observed at a dose of 100 μg/injection (P < 0.05). These experiments were performed at least five times. Data presented here represent a typical experiment. n, total number of animals used in this particular experiment; nap, total number of animals with paralysis in this particular experiment; hcs, highest clinical score observed in this particular experiment; do, day of onset.
