Figure 4.
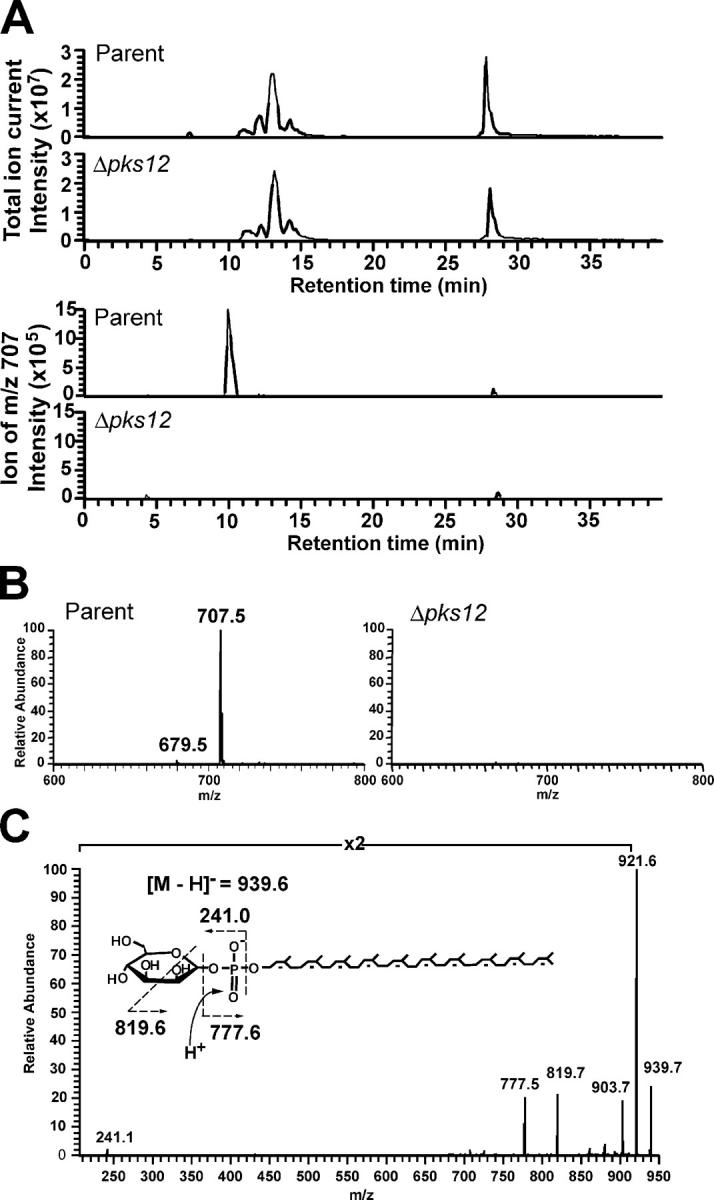
MPI and polyprenol biosynthesis pathways function independently. (A) Mass chromatograms of measured ions in the mass range corresponding to MPI (m/z 707.0–708.0; bottom) were compared with total ion chromatograms (top) in HPLC separation of phospholipids from M. tuberculosis H37Rv parental strain and the Δpks12 mutant. The total ion current trace shows that total phospholipid pattern was not substantially altered and confirms that similar amounts of lipids were analyzed for the comparison of m/z 707–708 ions. (B) Mass spectra at the retention time of 10 min in the chromatograms shown in A. The 100% relative abundance of the y axis was adjusted to the same intensity in each mass spectra from the parental and the mutant strains. (C) CDI-MS spectra of phospholipids from the Δpks12 mutant showed an ion of m/z 939.5, which corresponded to the expected mass and collision products of a true polyisoprenol phosphoglycolipid, mannosyl-β-1-phosphopolyisoprenol (C50 MPP). The ions of m/z 921.6 and m/z 903.7 corresponded to ones, which lost one or two water molecules from the parent ion and m/z 241.1 corresponded to a hexosyl phosphate ion.
