Figure 3.
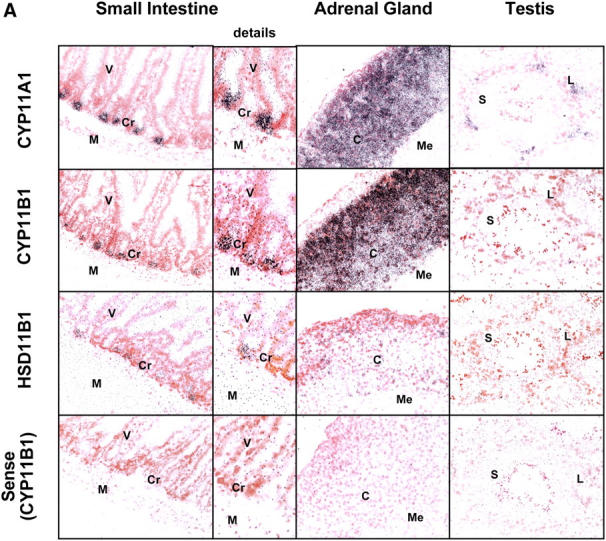
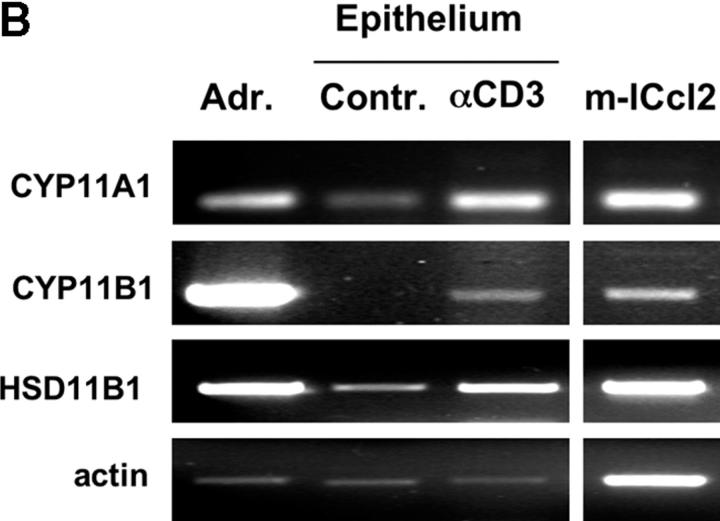
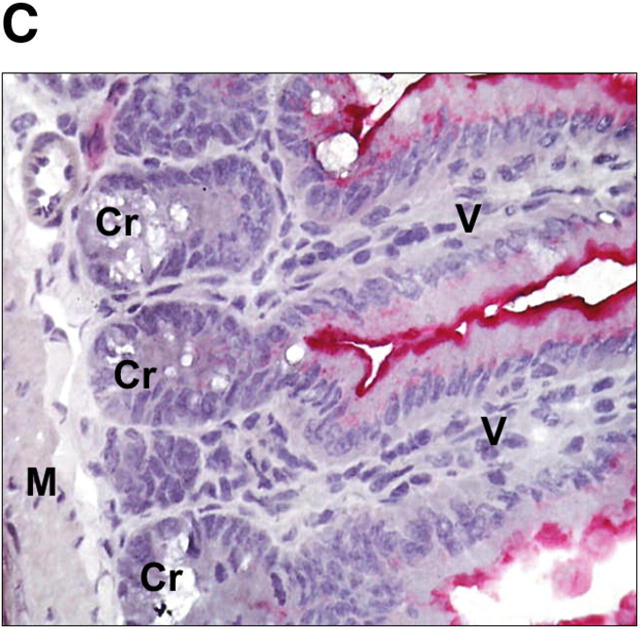
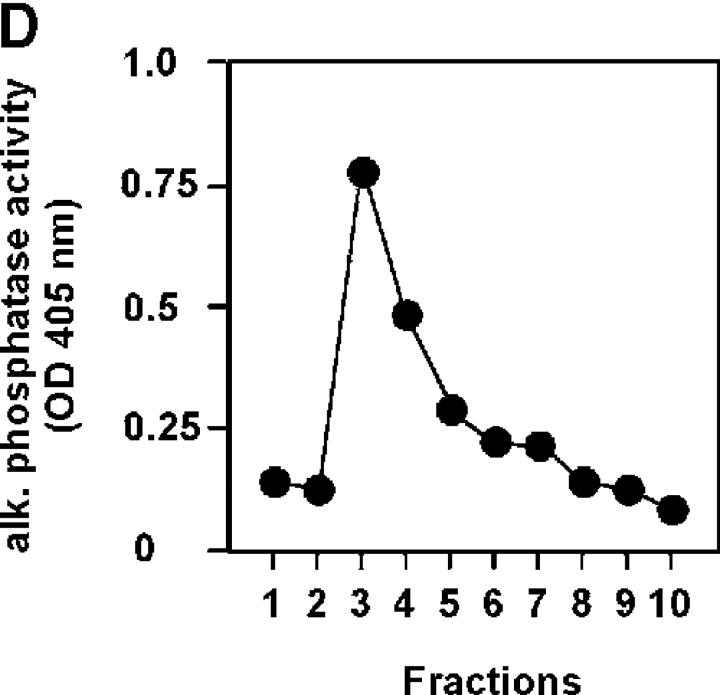
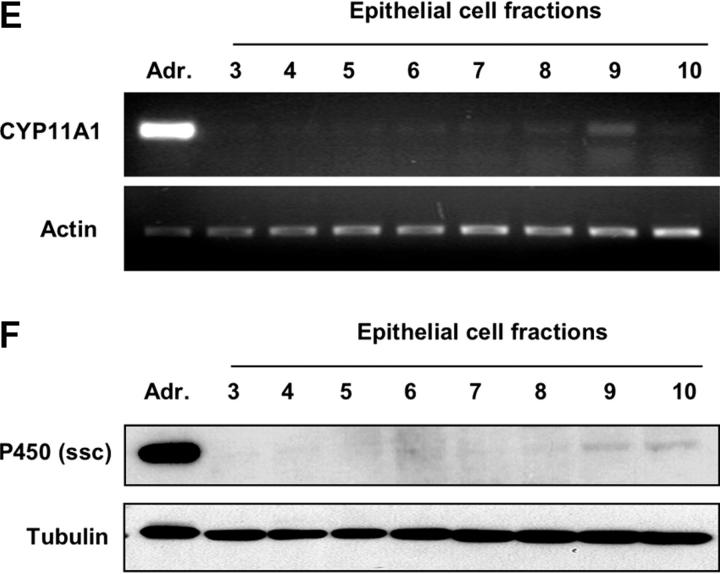
Localization of steroidogenic enzyme expression in small intestinal crypt cells. (A) In situ hybridization for steroidogenic enzymes. Tissue sections from small intestine, adrenal glands, and testis were hybridized with radiolabeled antisense probes for CYP11A1, CYP11B1, and HSD11B1. Unspecific binding was controlled using the CYP11B1 sense probe. M, muscularis; Cr, crypts; V, villi; C, cortex; Me, medulla; L, Leydig cells; S, Sertoli cells. A typical experiment out of two is shown. (B) Detection of steroidogenic enzyme expression in isolated epithelial cells. CYP11A1, CYP11B1, HSD11B1, and actin expression in adrenal glands (Adr.), isolated epithelial cells from control (contr.) and anti-CD3–injected mice (αCD3), or the murine epithelial crypt cell line m-ICc12 was assessed by RT-PCR. (C) Detection of endogenous alkaline phosphatase on small intestinal tissue sections. The luminal site of the epithelial layer stains red for alkaline phosphatase activity, whereas crypt cells are negative. V, villus; Cr, crypts; M, muscularis. (D) Analysis of alkaline phosphatase activity in differentially isolated epithelial cell fractions. Fraction 3 corresponds to the top villus fraction; fraction 10 corresponds to the bottom crypt cell fraction. (E) Analysis of CYP11A1 mRNA expression in the different epithelial cell fractions by RT-PCR. Equal amounts of RNA were confirmed by the detection of actin mRNA. (F) Detection of P450 (ssc) protein in the different epithelial cell fractions by Western blot. Equal protein loading was confirmed by the detection of tubulin.