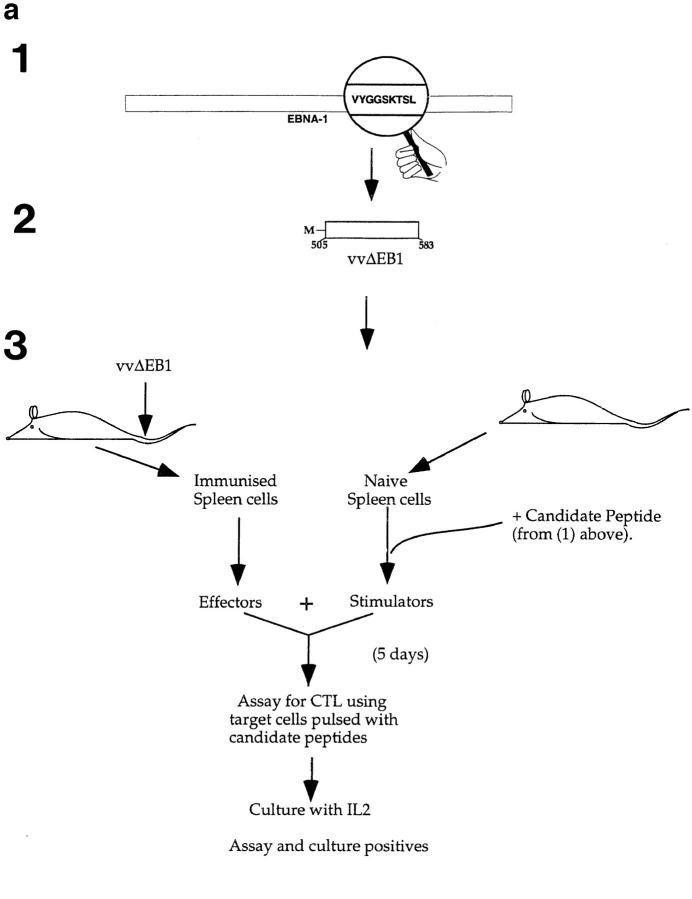
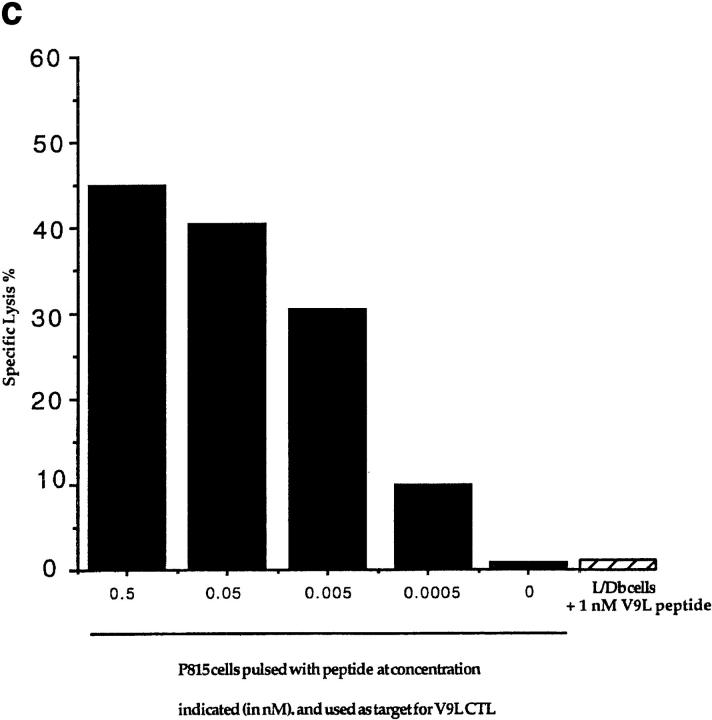
Figure 1.
(a) Scheme for rescue of peptide-specific CTLs by coculturing immunized splenocytes with naive splenocytes pulsed with candidate peptides (see text). (1) Identification of candidate epitopes. (2) Construction of vaccinia virus expressing the EBNA-1 (505–583) fragment (called VVΔEB-1) containing the candidate epitopes. (3) Immunization of mice and recovery of CTLs. (b) Mouse strains initially immunized with VVΔEB-1 and the peptides used to restimulate them in vitro. (Column 1) Candidate epitopes derived from the COOH-terminal of EBNA-1 using consensus motifs described in reference 13. (Column 2) Class I molecule for which the candidate peptide in column 1 carries the consensus motif (and strains immunized with VVΔEB-1). For example, VYGGSKTSL contains a Kd motif (i.e., Y at position 2, and L at position 9, underlined). Splenocytes from BALB/c mice (H2-d) immunized with VVΔEB-1 were restimulated with splenocytes pulsed with the V9L peptide, as described in a. Cocultures restimulated on peptides (as in column 1) were used as effectors in a Cr–release assay using peptide-pulsed cells as targets (see below for the target cells). (Column 3) Specific lysis above background in 51Cr release assays 5 d after in vitro restimulation with peptide-pulsed cells, was obtained for each of the effector cultures. Target cells used: P815 for all H2-d, L929 for H2-k, and EL-4 for H2-b. (c) V9L CTLs are peptide specific and MHC restricted. P815 cells were pulsed with the peptide dose indicated (in nM) and used as targets in Cr–release assay. K/T ratio was 20:1. Unpulsed cells (0 nM) are not lysed. Hatched bar shows L/Db cells that were pulsed with V9L peptide; these cells do not express Kd and were not lysed. The x-axis represents P815 cells pulsed with peptide at concentration indicated (in nM) and used as target for V9L CTLs.