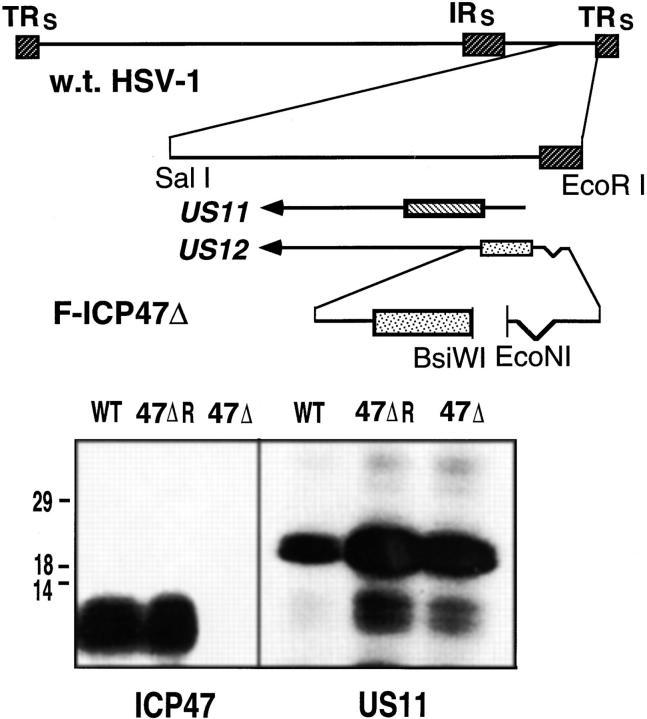
Figure 1.
Generation of an HSV-1 ICP47 deletion mutant. The genome of HSV-1 is depicted in the upper panel of the figure. A 100- nucleotide deletion in the HSV US12 gene, which encodes ICP47, was created. The deletion removes the ICP47 start codon and two downstream ATG codons, but does not affect the promoter of the adjacent US11 gene. Cells were cotransfected with a plasmid containing the deletion, and viral DNA derived from HSV-1 (strain F). Virus progeny were screened for the mutation by performing PCR on samples of viral DNA. A virus, denoted F-ICP47Δ, contained the deletion in the US12 gene. A rescued derivative of F-ICP47Δ, denoted F-ICP47ΔR, was produced by cotransfecting cells with F-ICP47Δ DNA and a plasmid containing the wild-type US12 gene. In the lower panel, cells were infected with wild-type HSV-1, F-ICP47Δ, or F-ICP47ΔR, then radiolabeled with [35S]methionine. ICP47 was immunoprecipitated from cell extracts using a rabbit anti-ICP47 serum, and US11 protein was immunoprecipitated using an anti-US11 serum.