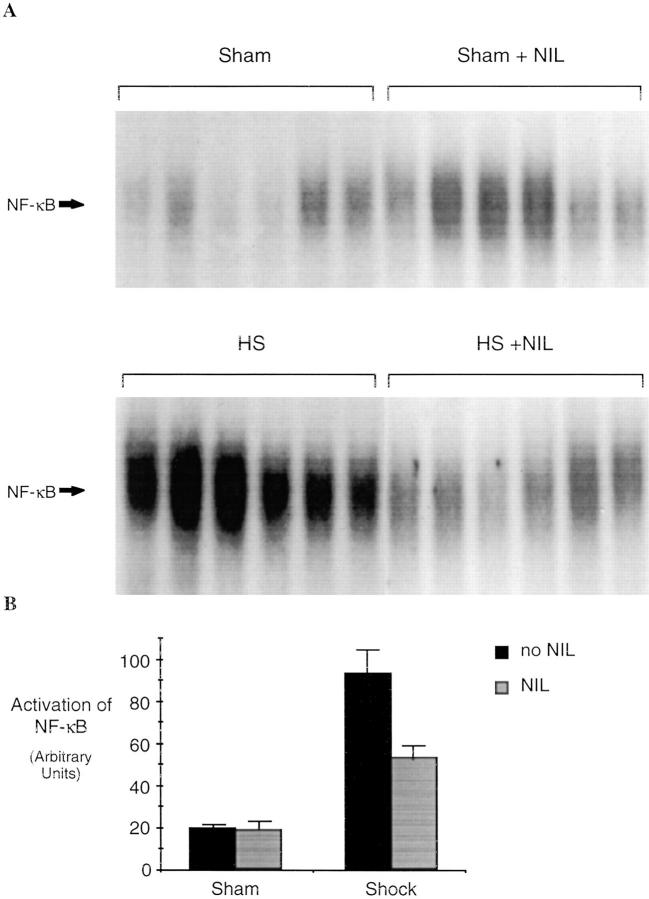
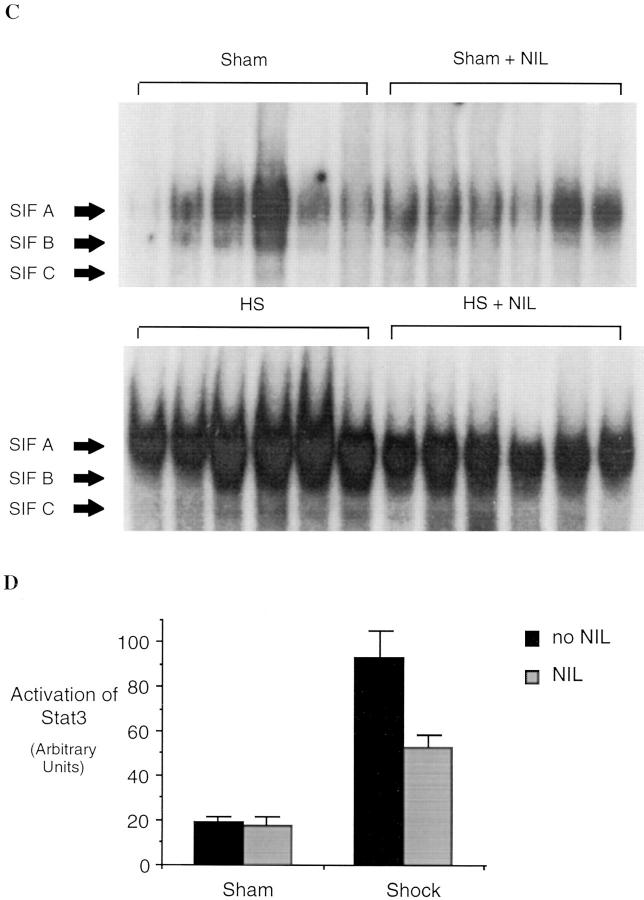
Figure 8.
Activation of NF-κB and Stat3 in the liver of rats subjected to hemorrhagic shock. In A, EMSA was performed using radiolabeled NF-κB duplex oligonucleotide (A) or radiolabeled hSIE (C) and 20 μg of protein extracts of shock and sham animals without or with L-NIL treatment. The positions of NF-κB and the SIF-A, -B, and -C complexes are indicated on the left. In B and D, the radioactive signal was quantitated by PhosphorImager analysis and the mean ± SEM plotted. The values shown are mean ± SEM. Black bars, untreated animals (n = 5); gray bars, L-NIL– treated animals. In shocked animals, the activation of NF-κB and the activation of Stat3 were increased significantly compared to sham animals (P = 0.002 and P = 0.001, respectively). after L-NIL treatment NF-κB activation was reduced 83% (P = 0.001) and activation of Stat3 was reduced 58% (P = 0.001) in shocked animals compared to untreated shock animals.