Figure 3.
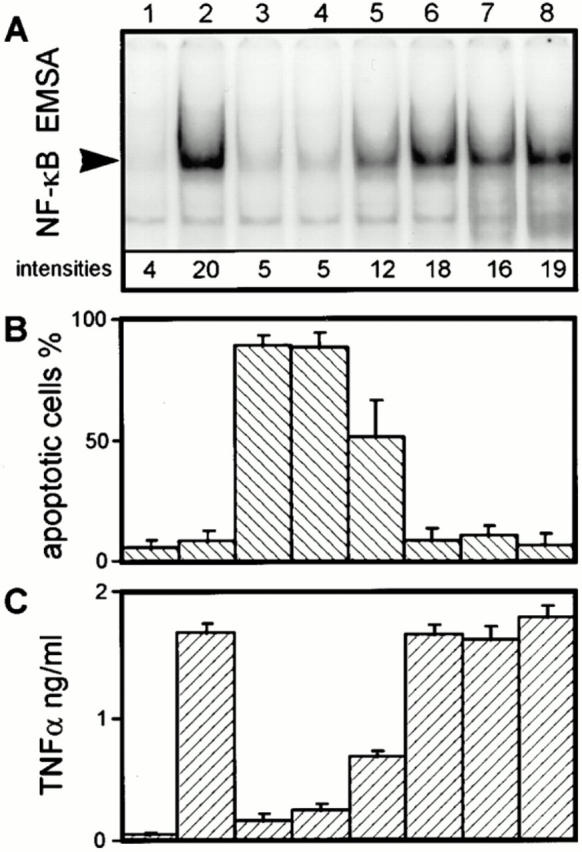
Correlation between inhibition of the NF-κB response, and apoptosis and TNF-α suppression in J774A.1 cells infected with different Y. enterocolitica mutants. (A) J774A.1 cell NF-κB activities. (B) Quantitation of J774A.1 cell apoptosis. (C) Quantitation of J774A.1 cell TNF-α production. J774A.1 cells were either untreated (lane 1), or infected with the virulence plasmid–cured strain WA-C (lane 2), the virulent wild-type strain WA-314 (lane 3), the YopH secretion-negative strain WA-C(pYV-7146) (lane 4), the yopO/yopP mutant WA-C(pYV-OP-1) (lane 5), the Yop secretion-negative strain WA-C(pYV-515) (lane 6), strain WA-C(pLCR) secreting YopD, YopB, YopN, and LcrV (lane 7), and strain WA-C(pLCR, pB8-23) secreting YopD, YopB, YopN, LcrV, YopH, and YopE (lane 8). (A) The NF-κB activities of J774A.1 cells were determined 60 min after infection by EMSA and quantified with a PhosphorImager. The radioactive intensities of the NF-κB DNA-binding activities are given below the respective NF-κB signal. This figure shows one experiment representative for three performed. Only sections of the autoradiogram containing the protein–DNA complexes are shown. (B) Apoptosis of J774A.1 cells was assayed 4 h after onset of infection by staining the cells with fluorescein-conjugated annexin V and propidium iodide, and counting apoptotic cells in a fluorescence microscope. (C) The TNF-α activities in the cell culture supernatants (dilution 1:40) were measured 150 min after the onset of infection, using a cytotoxic assay performed with the TNF-α–sensitive fibroblast cell line L929.
