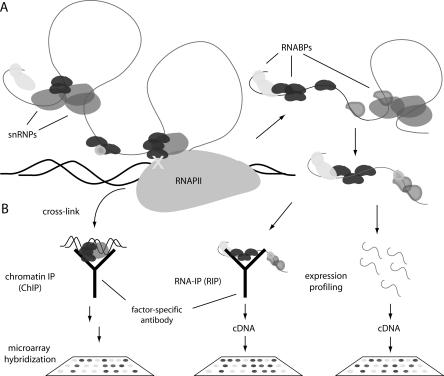
FIGURE 3.
Genome-wide profiling methods. (A) mRNA splicing begins during transcription in the nucleus, and finishes prior to nuclear export. RNABPs dynamically associate with transcripts throughout nuclear and cytoplasmic processing and transport steps. (B) Three methods to probe splicing regulation are shown, including ChIP and RIP analysis of a RNABP (black) and genome-wide transcript profiling. ChIP protocols cross-link (X) co-transcriptional processing factors to DNA, which is then profiled on microarrays. RIP involves purification of native or cross-linked RNPs and profiling associated transcripts. These methods can identify coregulated splicing networks. Expression profiling with splicing-sensitive microarrays generates a genome-wide survey of alternative splicing by measuring total, steady-state RNA.