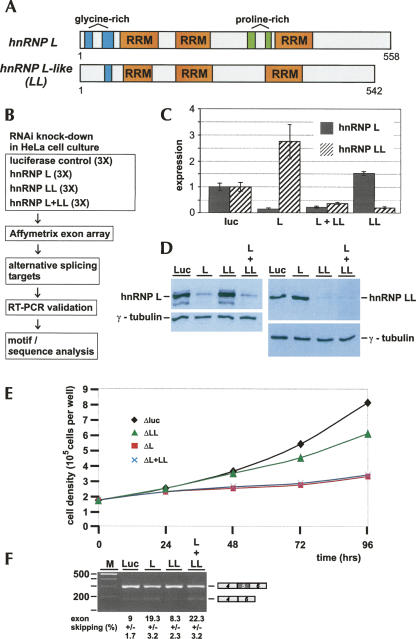
FIGURE 1.
Genome-wide search for hnRNP L-regulated alternative splicing targets: combined microarray/RNAi strategy. (A) hnRNP L and LL, two closely related RNA-binding proteins. The domain structures of hnRNP L (P14866; 558 amino acids) and LL (Q53T80; 542 amino acids) are schematically represented (three canonical RRM motifs as orange boxes; glycine- and proline-rich regions in blue and green, respectively). (B) Outline of microarray/RNAi strategy. (C,D) RNAi knockdown of hnRNP L and LL: validation by (C) quantitative RT-PCR and (D) Western blotting. HeLa cells were treated with siRNA oligonucleotides specific for hnRNP L, LL, both L and LL, or as a control, luciferase mRNAs. (C) Relative mRNA levels are diagrammed (filled bars, hnRNP L; striped bars, hnRNP LL), normalized to luciferase. (D) Lysates were prepared after knockdowns (as indicated above the lanes), and hnRNP L (left panel), hnRNP LL (right panel), and as internal standard, γ-tubulin (lower panels) were detected by Western blotting. (E) Growth curves of HeLa cell cultures after RNAi knockdown of hnRNP L, LL, and L/LL double knockdown. HeLa cell cultures were treated with siRNA oligonucleotides specific for hnRNP L (ΔL; red squares), hnRNP LL (ΔLL; green triangles), or both L and LL (ΔL + ΔLL; blue crosses); luciferase knockdown served as a control (Δluc; black diamonds). After 24, 48, 72, and 96 h, cell densities were measured. (F) Alternative splicing of endogenous GSTZ1 mRNA. Total RNA was prepared after knockdown in HeLa cells (as indicated above the lanes), and alternative splicing of endogenous GSTZ1 mRNA (exon 5 skipping, as schematically shown on the right) was assayed by semiquantitative RT-PCR; exon skipping is quantitated as a percentage below. (M) DNA size markers (DNA ladder mix; Fermentas).