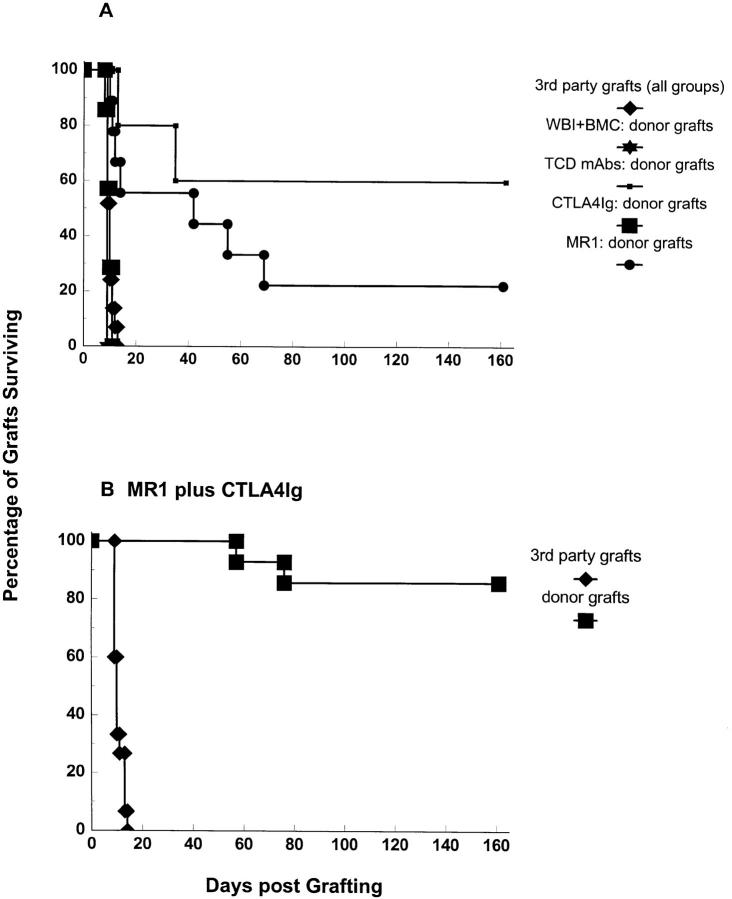
Figure 2.
Permanent survival of donor-specific skin grafts in chimeras prepared with 3 Gy WBI and allogeneic (B10.A) BM cells and treatment with MR1 plus CTLA4Ig. Combined results from two experiments are shown. Recipients were grafted with donor-specific (B10.A) and third party (A.SW) skin grafts at 3, 6, or 10 wk after BMT. Mice receiving the full treatment of BMT and MR1 plus CTLA4Ig accepted donor skin grafts (B) permanently (12 out of 14), with the exception of 2 animals that rejected their grafts at days 57 and 76, respectively. 9 grafts have been accepted in perfect condition for >110 d, and 5 grafts for >140 d. Third-party skin grafts (B) were rejected in the expected time frame (MST = 10 d). MR1 alone (A) led to prolongation of donor-specific skin graft survival (MST = 42 d), but only 2 out of 9 grafts survived >100 d. CTLA4Ig alone (A) failed to improve skin graft survival (n = 7, MST = 10 d). Control mice treated with 3 Gy WBI plus BMC (n = 4) and mice receiving 3 Gy WBI and MR1 plus CTLA4Ig alone (without BMT, data not shown) rejected donor skin within 2 wk. In a control group prepared with T cell–depleting mAbs on day −5 and day −1 plus BMT (plus 3 Gy WBI) (n = 5), donor skin grafts were permanently accepted in 60% of mice. Third party grafts were rejected within 2 wk in all groups.